Relation of severe COVID-19 in Scotland to transmission-related factors and risk conditions eligible for shielding support
1. Very high risk individuals that qualified for shielding interventions from COVID-19 were still at elevated risk for developing a severe infection.
2. Recent hospital exposures were the greatest risk factor for developing a case of severe COVID-19, among patients eligible for shielding interventions.
Evidence Rating Level: 3 (Average)
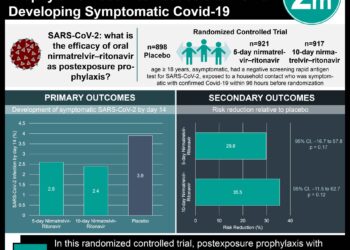
Towards the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, Scotland’s public health authorities created a list of conditions they deemed to be at moderate and very high risk for contracting the virus. For instance, patients that have had blood or bone marrow cancer, or patients on immunosuppression therapies, fell under the very high risk category. These high risk individuals and their households qualified for “shielding” interventions, such as free food and medication delivery services. The aim of this case-control study was to evaluate the shielding programme’s effectiveness by comparing the incidence of severe COVID-19 infections among shielded and non-shielded individuals, and identifying factors that increased the likelihood of severe COVID-19 within the shielding group. All 178,578 COVID-19 cases found in Scotland (from March 2020 to February 2021) were matched to 10 controls who had never been diagnosed with COVID-19, and shared the same sex and 1-year age range. They were classified into no risk, moderate risk, and very high risk categories. Out of the 212,702 individuals qualified for shielding, 2.9% received a diagnosis of COVID-19, 0.2% entered critical care, and 0.7% died. When compared to the no risk category, the severe COVID-19 rate ratio was 3.21 (95% CI 3.01-3.41, p < 0.001) for moderate risk and 6.3 (95% CI 5.8-6.8, p < 0.001) for very high risk (shielding eligible) patients. Within the shielding category, solid organ transplant patients were at the great risk, with a rate ratio of 13.4 (95% CI 9.6-18.8, p < 0.001). In terms of risk factors, a greater number of adults in a household, but not kids, was associated with higher risk for a severe infection within the shielding group. The strongest risk factor was recent hospital exposure, with a rate ratio of 6.0 (95% CI 4.7-7.7, p < 0001), with 45% of serious cases from shielding individuals having a recent hospital exposure. Overall, patients in the shielded category did experience higher risk for a severe COVID-19 infection, with the number of adults in a household and hospital transmissions being potential contributing factors to the elevated risk.
Click to read the study in BMC Medicine
Image: PD
©2021 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.