Saccadic eye movements predictive of surgical resident fatigue
Image: PD
1. Saccadic peak velocity magnitude during guided saccade tasks decreased with increased time-on-duty (mean precall = 0.634, mean postcall=0.619, P=0.04).
2. Time on duty did not affect saccadic peak velocity, nor did it affect performance during simulated laparoscopic tasks.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
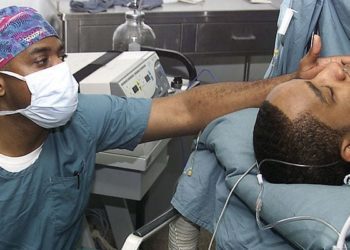
Study Rundown: Long work shifts and resident fatigue are frequent topics of debate when discussing patient safety and outcomes. Studies examining residents often report conflicting results due to the use of nonstandardized measures. This study found that increased time on duty decreased saccadic velocity, but did not affect residents’ performance with laparoscopic tasks. A head-mounted video eye tracker was used to examine the eye movements of general surgery residents during the performance of simulated laparoscopic surgery tasks and guided saccade tests, before and after their 24 hour call day. Limitations of this study include small sample size, as only 12 general surgery residents were examined. Moreover, residents were only evaluated at two points in time: precall and postcall. Thus, we are unable to find an exposure-response relationship for fatigue and saccade velocity. Finally, although laparoscopic simulation performance was not affected, it is a poor surrogate for measuring actual patient outcomes.
Click to read the study in Annals of Surgery
Relevant Reading: Fatigue among Clinicians and the Safety of Patients
In-Depth: This study examined 12 general surgery residents (6 men and 6 women) on the trauma service. Participants were tested at two levels of fatigue: precall and postcall. Each testing session was roughly 45 minutes duration. Examinees were tested on two simulated laparoscopic exercises (peg transfer task and precision cutting task), and two guided saccade tasks. Half of participants started with the precall condition, and half started with the postcall condition. Eye movements were recorded via a head-mounted video eye tracker, similar in configuration to a surgical headlight. Residents also completed two standardized questionnaires at the beginning of each testing session to evaluate fatigue, and continued to fill out a fatigue rating scale every 3 hours from the start of their call day.
Saccadic peak velocity magnitude during guided saccade tasks were decreased in the postcall condition compared to the precall condition (mean precall = 0.634, mean postcall=0.619, P=0.04). However, time-on-duty did not significantly affect saccadic peak velocity during the two simulated laparoscopic tasks. Precall vs postcall conditions did not affect execution times and expert evaluation of task performance during the simulated laparoscopic tasks. Subjective fatigue increased linearly across 24 hours of call, and residents reported feeling more tired during the postcall session than during the precall session.
By James Jiang and Chaz Carrier
More from this author: Deliberate practice in virtual reality simulator improves surgical resident performance, Laparoscopic hernia repair linked with lower rate of surgical infection, Study suggests general surgery residency graduates unprepared for fellowship, NEXUS Chest decision criteria sensitive for thoracic injury, Mortality after trauma increasingly due to preexisting conditions
© 2013 2minutemedicine.com. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2minutemedicine.com. Disclaimer: We present factual information directly from peer reviewed medical journals. No post should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors, editors, staff or by 2minutemedicine.com. PLEASE SEE A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IN YOUR AREA IF YOU SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE OF ANY SORT.