The PIONEER-HF Trial: Sacubitril-valsartan linked to superior outcomes in acute decompensated heart failure
1. Among patients hospitalized for acute decompensated heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), treatment with sacubitril-valsartan reduced N-terminal pro-B type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) greater than treatment with enalapril.
2. There was no significant difference in the rate of worsening renal function, hyperkalemia, symptomatic hypotension, or angioedema between either treatment group.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: While the landmark PARADIGM-HF trial demonstrated that the angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI) sacubitril-valsartan had superior clinical outcomes in patients with HFrEF compared to the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) enalapril, patients with acute decompensated HF were excluded. Given this population comprises a large part of clinical practice, the PIONEER-HF trial was conducted to analyze the efficacy and safety of ARNI therapy in patients with HFrEF hospitalized for acute decompensated HF. The authors reported a significantly greater reduction in NT-proBNP concentration, the primary outcome, in patients treated with sacubitril-valsartan compared to enalapril. Among key safety outcomes, there was no significant difference in the rates of worsening renal function, hyperkalemia, symptomatic hypotension, and angioedema between the sacubitril-valsartan and enalapril groups. The results of this trial extend the conclusions drawn from PIONEER-HF, and suggest ARNI therapy is a safe and effective strategy in HFrEF patients who present with acute decompensated HF.
This was a multicenter, randomized trial with a large and diverse patient population. It provided high level evidence of ARNI therapy in the inpatient HFrEF population, which was previously absent. The trial was limited by the high rate of medication discontinuation and high percentage of missing data. Furthermore, translation to clinical practice is limited by the strict requirements for sacubitril-valsartan initiation (including a 36-hour medication washout period) set by the authors, which may increase hospital stay. Future studies will need to look at potential outcome benefits of treatment with sacubitril-valsartan in patients with decompensated heart failure.
Click to read the study in NEJM
Click to read an accompanying editorial in NEJM
Relevant Reading: Angiotensin-neprilysin inhibition versus enalapril in heart failure
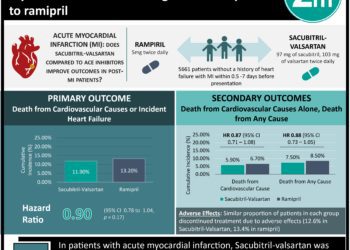
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: This was a multicenter trial that randomized 881 patients with HFrEF to sacubitril-valsartan (n=440) or enalapril (n=441) therapy. Primary outcome data, the time-averaged proportional change in the NT-proBNP concentration from baseline through weeks 4 and 8, was available for 349 (79.3%) of patients in the sacubitril-valsartan group and 348 (78.9%) in the enalapril group. Key safety outcomes included incidences of worsening renal function (increase in creatinine ³0.5 mg/dL and decrease in estimated glomerular filtration rate ³25%), hyperkalemia (³5.5 mmol/L), symptomatic hypotension, and angioedema.
Excluding discontinuation due to death, the trial medication was stopped early in 87 (19.6%) patients in the sacubitril-valsartan group and 90 (20.3%) patients in the enalapril group. The time-averaged reduction in NT-proBNP concentration obtained at weeks 4 and 8 was significantly greater in the sacubitril-valsartan group than enalapril group (percent change, -46.7% vs. -25.3%, respectively; ratio of change with sacubitril-valsartan vs. enalapril, 0.71; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.63 to 0.81; P<0.001). This result was evident by week 1 (ratio of change, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.69 to 0.85). There was no difference between the two treatment groups in the rates of worsening renal function (relative risk [RR] between sacubitril-valsartan vs. enalapril, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.67 to 1.28), hyperkalemia (RR, 1.25; 95% CI, 0.84 to 1.84), symptomatic hypotension (RR, 1.18; 95% CI, 0.85 to 1.64), or angioedema (RR, 0.17; 95% CI, 0.02 to 1.38).
Image: PD
©2019 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc