The REDUCE-IT trial: Icosapent ethyl reduces ischemic event risk in patients with hypertriglyceridemia despite statin use
1. After a median follow-up of 4.9 years, patients with elevated triglyceride levels despite statin use treated with icosapent ethyl had a lower risk of cardiovascular adverse events compared to patients in a placebo group.
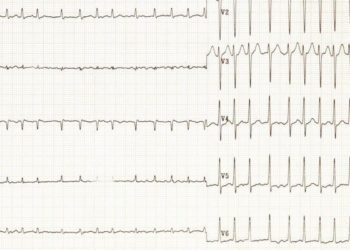
2. Hospitalization for atrial fibrillation or flutter occurred in more patients treated with icosapent ethyl compared to those in the placebo group.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Many patients with cardiovascular risk factors can maintain elevated triglyceride levels despite use of statins, and such hypertriglyceridemia is a notable risk factor for cardiovascular events. Many triglyceride lowering agents are not successful when used in addition to statins, necessitating a need to identify potential adjunct medications for patients with persistently elevated triglyceride levels. Icosapent ethyl has been shown to lower triglyceride levels when used as an adjunct agent in patients on a cardiovascular diet, though it’s potential to aid patients taking statins is unknown. The Reduction of Cardiovascular Events with Icosapent Ethyl–Intervention Trial (REDUCE-IT) evaluated patients with persistent hypertriglyceridemia despite statin therapy and showed a lower risk of cardiovascular events in patients taking icosapent ethyl compared to those in a placebo group. Icosapent ethyl treatment also significantly lowered triglycerides compared to patients in the placebo group.
This study provides a strong basis for the use of icosapent ethyl as a triglyceride lowering agent as an adjunct treatment in patients unresponsive to statin therapy. Strengths of the study include its randomized design, extensive subgroup analysis, and follow-up out to approximately 5 years. Limitations include use of a mineral oil in the placebo which altered statin absorption and not evaluating similar compounds in addition to icosapent ethyl, even on a more limited basis.
Click to read the study in NEJM
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: This multinational randomized controlled trial enrolled patients between 2011 and 2016. Eligible patients were 45 years or older with cardiovascular disease or multiple cardiovascular risk factors, and their triglyceride level was between 140 and 499 mg/dL and were on statin therapy for 4 weeks or longer. Notable exclusion criteria included severe heart, liver, or pancreatic disease, or a planned coronary procedure. Patients were randomized by cardiovascular risk stratum and geographic region to icosapent ethyl (n=4089) or placebo (n=4090) groups, and were followed to assess for a primary composite cardiovascular outcome consisting of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, or stroke. After a median follow-up of 4.9 years, patients in the icosapent ethyl group had triglyceride levels 18.3% lower compared to a 2.2% increase in the placebo group (median of 19.7% greater reduction from baseline in the treatment group, P<0.001). A composite cardiovascular outcome occurred in 17.2% of patients in the treatment group and 22.0% of patients in the placebo group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.75; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.68 to 0.83; P<0.001). The number needed to treat to avoid one composite cardiovascular outcome over 4.9 years was 21. The hazard ratio for a composite event was 0.72 (favoring the treatment group; 95% CI, 0.62–0.82) in males and 0.80 (95% CI, 0.62–1.03) in females. Hazard ratios for patients with baseline statin treatment in high and moderate intensity range favored the treatment group, while the hazard ratio was inconclusive for patients with low intensity baseline statin treatment. Overall rates of adverse events was similar between the trial groups, though rates of hospitalization for atrial fibrillation or flutter was higher in the treatment group.
Image: PD
©2019 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc