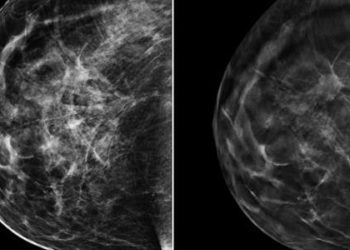
Tumor response ratio may predict survival following neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer
1. Tumor response ratio reflects the portion of the tumor remaining after the patient undergoes neoadjuvant chemotherapy prior to any surgical resection of the tumor.
2. In this study, the tumor response ratio was found to be predictive of overall survival in breast cancer patients who underwent neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Study Rundown: Current staging methods for breast cancer do not account for tumor response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC), which has assumed a more widespread role in recent years for the treatment of breast cancer. Previous studies have drawn an association between a pathologic complete response (pCR) to NAC and increased overall survival in breast cancer patients. The authors of this study attempted to predict the prognosis for those only with a partial response to NAC treatment. This was done by formulating a tumor response ratio (TRR) which is calculated by dividing the size of the residual primary tumor post NAC with the original size before the initiation of the treatment. The authors found that TRR was independently predictive of overall survival, with a larger TRR associated with decreased five year survival. While the study is significant in documenting a novel prognostic marker for breast cancer survival in patients undergoing NAC, the cohort reflects a small sample size at a single institution, limiting the generalizability of these results. A large appeal of TRR is its simplicity of focus on the size of the primary tumor, however its exclusion of lymphatic and other distant metastatic involvement may give reason to caution its predictive capability which may only be evident when applied to the study of a larger, more diverse breast cancer population. Other limitations include the seemingly arbitrary stratification of TRR groups, substation of ultrasound imaging when MRI’s were not available, and limited time of follow-up.
Click to read the study in the Annals of Surgical Oncology
Relevant Reading: Clinical course of breast cancer patients with complete pathologic primary tumor and axillary lymph node response to doxorubicin-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy
In-Depth [retrospective cohort]: A total of 218 patients with stage I to III primary breast cancer who underwent NAC with sufficient pre-treatment imaging at City of Hope from 1997 to 2010 were included in the study. Patients were stratified into four distinct groups based on their tumor response to NAC: TRR = 0 (pathologic complete response, pCR), 0 < TRR < 0.4 (strong partial response, SPR), .4 < TRR < 1.0 (weak partial response, WPR), and TRR > 1 (tumor growth, TG). Five year survival was 90% of the pCR group, compared to 79% in SPR, 66% in WPR, and 60% in TG. TRR was found to be independently predictive of overall survival (p = 0.0035) while more traditional methods of staging: pathologic (p = 0.23) and pre-NAC clinical tumor (p = 0.87) were not. The predictive capability of TRR was maintained after accounting for potential confounders (p = 0.016).
More from this author: Risk of delayed-onset ulnar neuritis after arthroscopic release of elbow contracture, Somatostatin may not reduce risk of pancreatitis post endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, Meniscal allograft transplantation may improve knee function
Image: PD
©2012-2014 2minutemedicine.com. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2minutemedicine.com. Disclaimer: We present factual information directly from peer reviewed medical journals. No post should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors, editors, staff or by 2minutemedicine.com. PLEASE SEE A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IN YOUR AREA IF YOU SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE OF ANY SORT.

![2MM: AI Roundup- AI Cancer Test, Smarter Hospitals, Faster Drug Discovery, and Mental Health Tech [May 2nd, 2025]](https://www.2minutemedicine.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/Untitled-design-350x250.png)