Use of mobile devices for calming associated with increased emotional reactivity in some children
1. In a prospective longitudinal study, the use of mobile devices for calming was associated with altered emotional reactivity and executive functioning in young boys.
2. The association of mobile device use with altered emotional reactivity and executive functioning was increased in children with higher surgency temperament characteristics.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Study Rundown: Early childhood is a critical time for developing neurocognitive processes such as executive functioning (EF) and emotional reactivity (ER). Deficits in these neurocognitive domains are prominent in disorders such as attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Previous research suggests that television time and total screen time may lead to deficits in EF, although the use of mobile devices that provide on-demand handheld access has been not been rigorously studied. This study addressed this shortcoming by enrolling parent-child pairs in a prospective cohort study to evaluate the association between parent-reported frequency of use of mobile devices to calm children when upset and EF and ER measures at baseline, 3-month, and 6-month follow-up. In males, the use of mobile devices to calm was associated with lower EF (at baseline) and higher ER measures (at all time points). The association between mobile screen use and altered EF and ER was also present in children with higher temperamental surgency. Significant limitations of this study include the use of a single question to measure mobile device use and the short follow-up period. In general, this study provides evidence that frequent mobile screen use for calming young children may alter neurocognitive processes such as executive functioning and emotional reactivity, and alternative calming methods may be more appropriate.
Click here to read the article in JAMA Pediatrics
Relevant Reading: Risk factors for internalizing and externalizing problems in the preschool years: systematic literature review based on the child behavior checklist
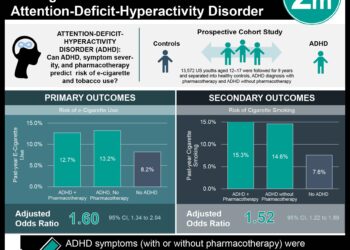
In-Depth [prospective cohort]: Following enrollment, 422 parent-child pairs were recruited and included English-speaking parents of typically developing children aged 3 to 5 years. Data collection occurred at baseline (T1), with 3-month (T2) and 6-month follow-up (T3). The primary exposure was the frequency of device use for calming purposes as assessed by the Comprehensive Assessment of Family Media Exposure (CAFE) survey. Parent-reported outcomes included (1) executive functioning measured by the Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function–Preschool Version (BRIEF-P) scales, and (2) emotional reactivity measured by the Child Behavior Checklist–Preschool (CBCL-P) scale. Covariates included age, sex, race, ethnicity, preschool or childcare enrollment, prematurity, parental demographics, and childhood temperament. A child’s surgent temperament was evaluated using the parent-measured Rothbart Child Behavior Questionnaire–Very Short Form. Both BRIEF-P and CBCL-P scales showed within-person stability over time. When data were stratified by sex, there was no significant correlation between mobile use and EF or ER measures at any time point in female participants. In contrast, males had a correlation between EF measures and the use of devices at T1 (r =0.33, 95% CI, 0.21-0.46; P<0.001), but not T2 or T3 timeframes. ER was also correlated with mobile use at all time points in males. When results were stratified by child temperament, children with high surgency traits, use of devices to calm at the T2 time point was associated with higher ER at the T3 timepoint (r = 0.11; 95% CI, 0.01-0.22).
Image: PD
©2023 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.