Vemurafenib linked to therapeutic effect in various cancers
1. Participants with BRAF V600 mutation-positive small-cell lung cancer, Erdheim Chester Disease (ECD) and Langerhan’s-Cell Histiocytosis (LCH) demonstrated a modest but statistically significant response rate to treatment with vemurafenib.
2. Participants with BRAF V600 mutation-positive colorectal cancer did not demonstrate appreciable response rates to vemurafenib monotherapy or vemurafenib with cetuximab on a whole.
Evidence Rating: 2 (Good)
Study Rundown: BRAF V600 mutations that result in constitutively active downstream MAPK pathways are found in approximately half of all cutaneous melanomas. The recently developed BRAF kinase-inhibitor, vemurafenib, has shown promising antitumor effects and improved survival in BRAF V600 mutation-positive melanomas. Although ongoing genomic research has identified this mutation in a sizeable number of nonmelanoma cancers, the efficacy of vemurafenib in treating these cancers has not been fully explored. This study aimed to investigate the preliminary clinical efficacy of vemurafenib in seven cohorts grouped by type of BRAF V600-mutaiton nonmelanoma cancer.
Of the seven cohorts treated with vemurafenib, including non-small-cell lung cancer, ECD-LCH, cholangiocarcinoma, ovarian cancer, multiple myeloma and colorectal cancer, and “all others” – only non-small-cell lung cancer and ECD-LCH groups showed significant response above baseline tumor burden. These data suggest that different cancers with a common biomarker, such as BRAF V600 mutations, may respond differently to targeted therapy. While the primary limitation of this study is small sample size, overall, this “basket” study design offers a novel approach to clinical trials: a means by which to identify a favorable response to a targeted therapy in a small group of heterogeneous patients.
Click to read the study, published today in NEJM
Relevant Reading: Basket Trials and the Evolution of the Clinical Trial Design in an Era of Genomic Medicine
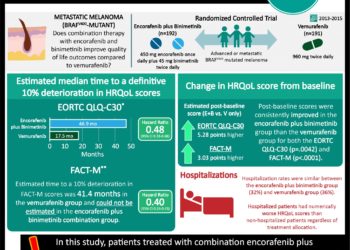
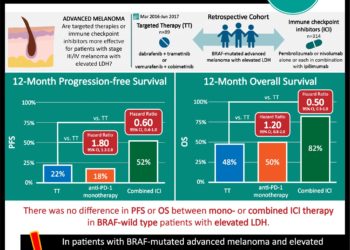
In-Depth: [prospective cohort]: In this ongoing prospective, multi-cohort, “basket” study, 122 participants with BRAF V600 mutation-positive cancers were enrolled from 23 centers worldwide. All patients received vemurafenib at 960 mg PO BID with the exception of the colorectal cancer cohort. That cohort was divided into a vemurafenib monotherapy versus a combined vemurafenib with cetuximab group. The primary outcome for all groups included disease response rate at 8 weeks based on Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) criteria for solid tumors and IMWG criteria for multiple myeloma. At 8 weeks, 15% response rate was considered low and 35% and 45% were considered efficacious, with 45% being a “high” efficacious response. The secondary end points included progression-free and overall survival. For non-small-cell lung cancer, the objective response rate was 42% (95% CI, 20 – 67). Patients in the ECD-LCH cohort demonstrated at 43% response rate (95% CI, 18 – 71). For the colorectal cancer cohort, the vemurafenib monotherapy arm showed zero response to treatment, while the combination therapy arm had a response rate of 4% (95% CI, <1 – 20). For colorectal cancer patients receiving monotherapy, the median progression-free survival and overall survival were 4.5 months (95% CI, 1.0 – 5.5) and 9.3 months (95% CI, 5.6 to not reached), respectively. In the combination group, the median progression-free survival and overall survival were 3.7 (95% CI, 1.8-5.1) and 7.1 months (95% CI, 4.4 to not reached), respectively. The most common adverse events among all patients receiving monotherapy were rash (68% of patients), fatigue (56%), and arthralgia (40%).
Image: PD
©2015 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.