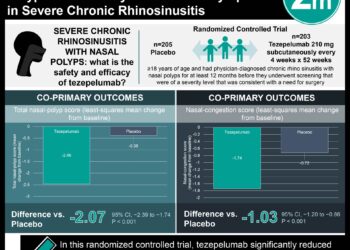
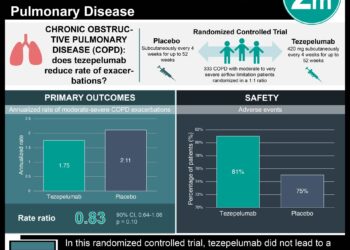
#VisualAbstract: Tezepelumab reduced annual exacerbation rates in patients with severe asthma
1. Subcutaneous tezepelumab treatment was shown to reduce the rate of annual asthma exacerbations in patients with severe asthma compared to the placebo group.
2. No significant differences in adverse events were found between the treatment and control groups.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: In patients with severe asthma, thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) is a cytokine that exacerbates airway obstruction and increases airway inflammation. The cytokine can be blocked with the monoclonal antibody called tezepelumab. As such this trial, investigated the efficacy of tezepelumab to reduce the annual rate of asthma exacerbations. The study determined Tezepelumab treatment significantly reduced the annual rate of asthma exacerbations compared to the placebo treatment. Additionally, tezepelumab improved prebronchodilator 1-second forced expiratory volume (FEV1). No differences were found in both groups for the proportions of patients reporting adverse events with the most common event being upper respiratory tract infection. The study was limited by the strict inclusion criteria and the small number of adolescent patients included in the study. Nonetheless, the findings are still significant as the study provided evidence for the potential benefit of tezepelumab in severe asthma over multiple measures from exacerbation rates to lung function.
Click to read the study in NEJM
Relevant Reading: Tezepelumab as an Emerging Therapeutic Option for the Treatment of Severe Asthma: Evidence to Date
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: This randomized control trial across 297 sites in 18 countries enrolled 1,061 patients between the ages of 12 and 80 with severe asthma. Inclusion criteria were patients with diagnosed severe asthma for at least 12 months, an FEV1 of less than 80% of its predicted value, and a minimum of two asthma exacerbations required hospitalization. Patients who were smokers were not included in the study. The patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive tezepelumab or placebo, respectively, every four weeks for 52 weeks. The primary outcome was the annual asthma exacerbations rate. The study determined the annual asthma exacerbation rate was reduced to 0.93 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.80 to 1.07) in the treatment group compared to 2.10 in the placebo group (95% CI, 1.84 to 2.39) (rate ratio, 0.44; 95% CI, 0.37 to 0.53; P<0.0001). Furthermore, patients receiving tezepelumab (0.23 liters) showed improvement in the prebronchodilator FEV1 compared to the placebo group (0.09 liters) (difference, 0.13 liters; 95% CI, 0.08 to 0.18; P<0.001. Similar proportions of both groups experienced adverse events with the most common severe event being nasopharyngitis, headache, and upper respiratory tract infections. Together, this study demonstrated the benefit of tezepelumab in improve symptom control and improve quality of life in patients with severe asthma.
©2021 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.