#VisualAbstract: COVID-19 vaccines provided durable protection from COVID-19, but their effectiveness waned over time in North Carolina
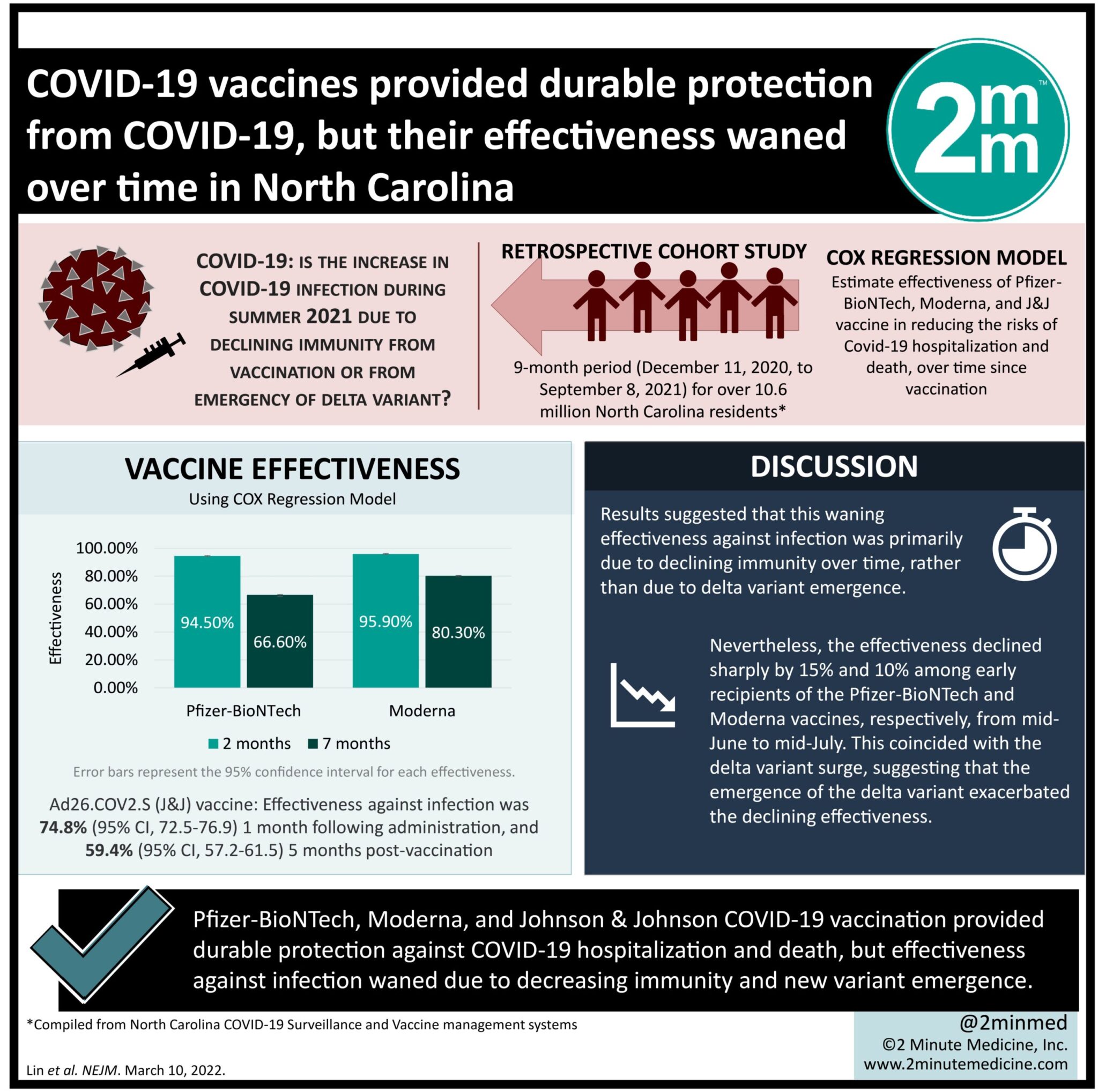
1. Three Covid-19 vaccines from Pfizer, Moderna, and Johnson & Johnson provided durable protection against hospitalization and death.
2. However, effectiveness against infection waned due to decreasing immunity and new variant emergence.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Study Rundown: There has been a resurgence of Covid-19 cases in the United States, but its cause, whether due to waning vaccine effectiveness over time or emergence of new variants, remains unclear. The current study examined vaccination and outcome data for Covid-19 during a 9-month period (December 2020-September 2021) for North Carolina residents. The three vaccines of interest were BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech), mRNA-1273 (Moderna), and Ad26.COV2.S (Johnson & Johnson-Janssen) and their effectiveness in reducing the risks of infection, hospitalization, and death were estimated from this database. It was found that all three vaccines were effective in reducing these risks, but protection against hospitalization and death was sustained better than against infection, which declined over time. Furthermore, the two mRNA vaccines conferred higher protection than the adenovirus-based Ad26.COV2.S. The observational study showed that for North Carolina residents, all three Covid-19 vaccines provided lasting protection against hospitalization and death, despite waning protection against infection. The rising infection rate was attributed to both declining immunity and the emergence of the B.1.617.2 Delta variant.
Click here to read the study in NEJM
Relevant Reading: Effectiveness of mRNA BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine up to 6 months in a large integrated health system in the USA: a retrospective cohort study
In-Depth [retrospective cohort]: This retrospective cohort study examined Covid-19 vaccination and outcomes over a 9-month period (December 11, 2020, to September 8, 2021) for 10.6 million North Carolina residents. This data was compiled from the North Carolina Covid-19 Surveillance and Vaccine Management systems. The three vaccines of interest were BNT162b2, mRNA-1273, and Ad26.COV2.S. The outcomes of interest were Covid-19 infection (either symptomatic or asymptomatic), and Covid-19-related hospitalization and death. The effectiveness of the vaccines over time was evaluated based on a Cox regression model and compared against the unvaccinated population. The mRNA vaccines, BNT162b2 (30µg per dose) and mRNA-1273 (100µg per dose) were evaluated following one and two doses, whereas the adenovirus-based Ad26.COV2.2 (5 x 1010 viral particles) was evaluated following one dose, in accordance with the manufacturer’s regimens. It was found that two doses of BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 provided effectiveness rates against infection of 94.5% (95% confidence interval [CI], 94.1-94.9) and 95.9% (95% CI, 95.5-96.2), respectively at 2 months after the first dose was administered. At 7 months, however, their effectiveness against infection declined to 66.6% (95% CI, 65.2-67.8) and 80.3% (95% CI, 79.3-94.9). For the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine, its effectiveness against infection was 74.8% (95% CI, 72.5-76.9) at 1 month following administration and fell to 59.4% (95% CI, 57.2-61.5) at 5 months post-vaccination. By considering the varying times of vaccination, the results suggested that this waning effectiveness against infection was primarily due to declining immunity over time, rather than a specific period of delta variant emergence. Nevertheless, the effectiveness was observed to decline sharply by 15% and 10% among early recipients of BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 (first dose given before March 2021), respectively, from mid-June to mid-July, which coincided with the delta variant surge. This suggested that the emergence of the delta variant exacerbated the declining effectiveness. Protection against hospitalization and death, however, was sustained better for all three vaccines. Specifically, the BNT162b2 conferred the effectiveness against hospitalization and death of 96.4% and 98.0% at 2 months, respectively; and 88.7% and 90.5% at 7 months. The mRNA-1273 effectiveness against hospitalization and death was 97.2% and 98.6% at 2 months and maintained at 94.1% and 95.5% at 7 months. The Ad26.COV2.S effectiveness against hospitalization and death was 85.8% and 85.95% at 2 months and remained higher than 80% and 70%, respectively, at 6 months. Similar to infection prevention, the effectiveness of BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 against hospitalization and death was declining during the emergence of the Delta variant. The vaccine effectiveness as estimated by the current study was consistent with efficacy results from phase 3 clinical trials as well as cohort studies internationally. Despite its observational nature, its large sample size provided strong evidence that the effectiveness of Covid-19 vaccines waned over time, significantly more so for infection than hospitalization and death, and this decline was further exacerbated by the emergence of the new variant.
©2022 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.