#VisualAbstract:Complete revascularization reduces mortality in older adults with myocardial infarction
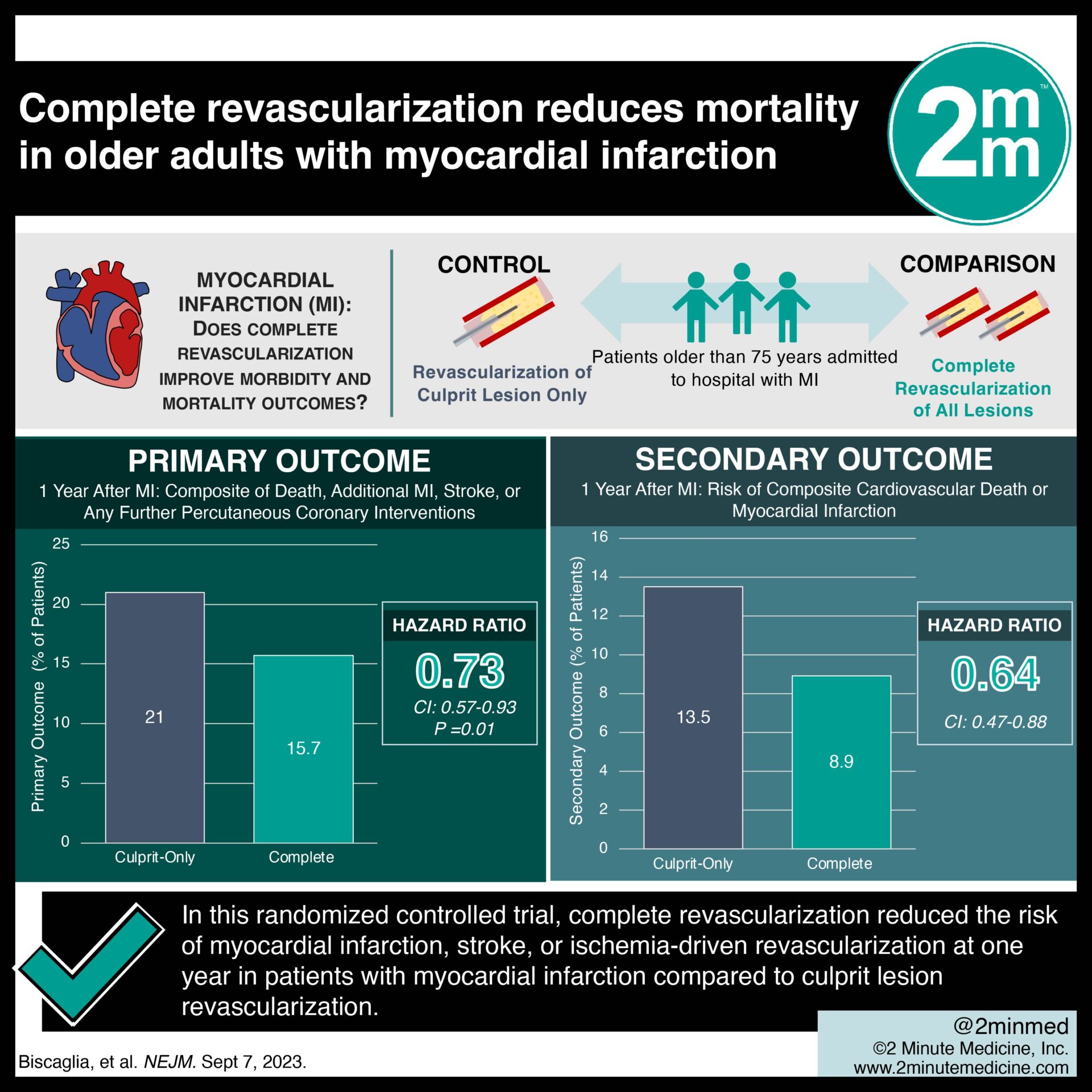 1. In this randomized controlled trial, complete revascularization reduced the risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, or ischemia-driven revascularization at one year in patients with myocardial infarction compared to culprit lesion revascularization.
1. In this randomized controlled trial, complete revascularization reduced the risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, or ischemia-driven revascularization at one year in patients with myocardial infarction compared to culprit lesion revascularization.
2. There was no difference in safety outcomes, including acute kidney injury, stroke, or bleeding, between groups.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: The decision process surrounding the management of myocardial infarction in older adults is challenging. When considering the rate of complications and adverse outcomes, one such difficulty is deciding whether it is beneficial to revascularize all lesions or just the culprit lesions during percutaneous coronary intervention. This randomized controlled trial evaluated the morbidity and mortality outcomes of complete revascularization versus revascularization of a culprit lesion following myocardial infarction amongst adults older than 75. Results of the primary study found that complete revascularization was significantly associated with lower risks of death, stroke, myocardial infarction, and additional need for revascularization at one year compared to revascularization of a culprit lesion only. There were no significant differences in safety outcomes between the two groups. A key limitation of this study was the open-label design of the trial whereby both patients and physicians were aware of initial angiographic results. Further, the results cannot be directly generalized to angiography-guided complete revascularization. In summary, this study supported complete revascularization in the management of myocardial infarction within adults older than 75 years old.
Click to read the study in NEJM
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: This was an open-label randomized trial comparing morbidity and mortality outcomes between complete revascularization revascularization of culprit lesions during a myocardial infarction. The primary outcome of interest was a composite of death, additional myocardial infarction, stroke, or any further percutaneous coronary interventions one year after the initial event. Participants older than 75 years old admitted to hospital due to either a myocardial infarction with ST-elevation on electrocardiogram (ECG), or a myocardial infarction without ST-elevation on ECG were included in the study. Participants who had not undergone successful revascularization of the culprit lesion, did not have a clear culprit lesion, did not have at least one lesion in a non-culprit artery, or did not have an estimated life expectancy of at least one year were excluded. After applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 1,445 patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive either complete revascularization of all lesions or revascularization of the culprit lesion only. Primary results of the analysis found that complete revascularization resulted in a significantly higher rate of primary outcomes at one year compared to revascularization of culprit-only lesions (hazard ratio, 0.73; 95% Confidence Interval [CI], 0.57 to 0.93; p=0.01). Results of the secondary analysis found that there were no differences in safety outcomes such as acute kidney injury, stroke, or bleeding. Similarly, complete revascularization had a significantly lower risk of composite cardiovascular death or myocardial infarction at one year compared to revascularization of culprit-only lesions (hazard ratio 0.64; 95% CI, 0.47 to 0.88). Overall, this study provided evidence that complete revascularization is associated with lower risks of composite myocardial infarction, stroke, or ischemia-driven revascularization in older adults post-myocardial infarction.
©2023 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.