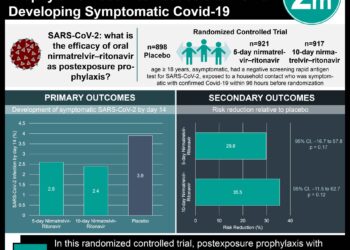
#VisualAbstract: Healthcare workers at higher risk of COVID-19 compared to the general population
1. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies was generally low in healthcare workers but higher than the general population.
2. Loss of taste or smell was most strongly associated with seropositivity in healthcare workers.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Study Rundown: Healthcare workers comprised a significant proportion of individuals who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 in European countries severely hit by COVID-19, including Italy and Spain. Surveillance of the burden of seropositive disease among healthcare workers compared to the general population was unclear, as was which groups were at highest risk of seropositivity.
This observational cohort study included 28,972 health-care workers and 4672 blood donors from the Capital Region of Denmark who were tested for SARS-CoV-2 IgG and IgM antibodies using a point-of-care test. Results suggested that while the seroprevalence was generally low in both groups, there was significantly a significantly higher burden of seropositivity among healthcare workers compared with blood donors, who served as a proxy for the general population. Among healthcare workers, frontline workers in hospitals had a significantly higher seroprevalence of infection than their non hospital-based counterparts. Loss of taste or smell was the symptom most strongly associated with seropositivity, with fever also strongly associated.
This study was limited by the fact that healthcare workers were not blinded to the test result when filling out symptom questionnaires, introducing bias in symptom reporting. Additionally, blood donors were healthy individuals screened for travelling abroad or having a fever, and may have a different seropositivity than the general population. Nonetheless, this study represents the largest effort to date to determine SARS-CoV-2 seropositivity comparing healthcare providers and the general population.
Click to read the study in The Lancet Infectious Diseases
Relevant Reading: SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence in COVID-19 hotspots
In-Depth [retrospective cohort]: This study included 28,972 health-care workers (mean age 44.4 years, 78.9% female) employed in the Capital Region of Denmark who considered themselves to have any work-related patient contact. SARS-CoV-2 IgG and IgM antibodies were tested in whole blood via a lateral flow assay point-of-care test administered independently in each clinical department. After test results were received, participants completed an online survey regarding demographics, type of work, symptoms of COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2 screening results. 4,672 blood donors (mean age 40.7 years, 53.55% female) in the same region were screened with the same point-of-care test for comparative purposes; the group represented a proxy for the general population.
Overall, seroprevalence was estimated at 4.04% (95% CI 3.82 to 4.27) amongst healthcare workers. Of these, 2.81% (95% CI 2.63 to 3.00) developed IgM antibodies, 2.67% (95% CI 2.49 to 2.86) developed IgG antibodies and 1.43% (95% CI 1.30 to 1.58) developed both IgM and IgG antibodies. Among the blood donors, seroprevalence of either IgG or IgM antibodies was 3.04% (95% CI 2.58 to 3.57), significantly lower than healthcare workers (relative risk (RR) [healthcare workers versus blood donors] 1.13, 95% CI 1.12 to 1.58, p=0.0008). Frontline healthcare workers in hospital settings had higher seroprevalence compared to healthcare workers in other settings (4.55% vs 3.29%; RR 1.38, 95% CI 1.22 to 1.56, p<0.001). Having any symptom of COVID-19 in healthcare workers was associated with greater seroprevalence compared to asymptomatic workers (5.86% vs 1.92%; RR 3.05, 95% CI 2.88 to 3.50, p<0.001). Of these symptoms, loss of smell or taste was the symptom most associated with seropositivity (32.39% vs 2.84%, RR 11.38, 95% CI 10.22 to 12.68).
©2020 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.