Bariatric surgery linked to reversal of diabetes
Image: PD
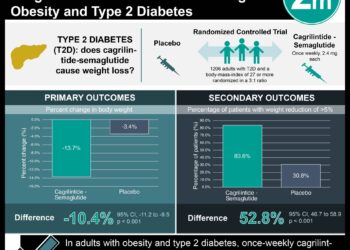
1. 50% of patients with type II diabetes who underwent bariatric surgery achieved complete or partial remission after five years of follow-up. This was associated with a shorter duration of pre-operative diabetes and a higher degree of lasting weight loss.
2. Patients whose diabetes recurred demonstrated improved glycemic, blood pressure and lipid control.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Study Rundown: Analysis of records and post-operative follow-up for type II diabetic patients who underwent bariatric surgery demonstrated remission or unequivocal improvement of metabolic syndrome. Authors took great care to arrange follow-up for patients either at their clinic or with the patient’s primary care doctor. It is possible that this could have introduced some variability and bias into the study, however it is unclear what percentage of patients required visits outside of the study clinic. Overall, this study was well-designed with a large patient cohort, rigorous follow-up and clear outcome end-points.
Click to read the study in Annals of Surgery
Relevant Reading: Reduction in Incidence of Diabetes, Hypertension and Lipid Disturbances after Intentional Weight Loss Induced by Bariatric Surgery: the SOS Intervention Study
In-Depth [retrospective cohort]: This study analyzed 217 type II diabetic patients who underwent bariatric surgery including sleeve gastrectomy, gastric banding and roux-en-y gastric bypass between 2004 and 2007. Fifty percept of the patients achieved long-term complete (24%) or partial (26%) type II diabetes remission. Only 16% did not see improvement glycemic control, while the remaining 34% experienced improved glycemic control. Gastric bypass patients experienced more weight loss and lower diabetes remission rates than laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy or laparoscopic gastric banding. Additionally, gastric bypass was associated with diabetes remission after multivariable analysis, along with shorter duration of diabetes and greater weight loss. Even patients with recurrence demonstrated improved diabetes metrics including significantly lower HbA1C, fasting blood sugar and use of insulin. They also reached American Diabetes Association goals of glycemic control, blood pressure control and LDL control in greater numbers.
By Asya Ofshteyn and Allen Ho
More from this author: Postoperative readmission rates correlated with length of stay and ASA class, Prompt surgery may yield better outcomes for adhesive small bowel obstruction, Immediate cholecystectomy preferred treatment for acute cholecystitis, Living donor outcomes improved by motivational interviewing, Pancreatic islet autotransplantation a potential treatment for malignant disease
© 2013 2minutemedicine.com. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2minutemedicine.com. Disclaimer: We present factual information directly from peer reviewed medical journals. No post should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors, editors, staff or by 2minutemedicine.com. PLEASE SEE A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IN YOUR AREA IF YOU SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE OF ANY SORT.