Continuous glucose monitoring associated with better glucose control for patients receiving insulin for type 2 diabetes
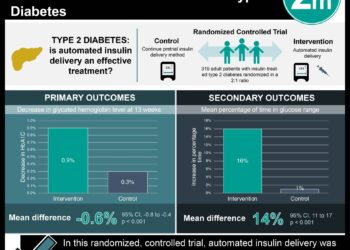
1. Continuous glucose monitoring in type 2 diabetes patients was associated with improved glycemic control.
2. No significant difference in quality-of-life was observed in patients using continuous glucose monitoring.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has been well studied in type 1 diabetes patients; however, little data exists regarding its efficacy in patients with type 2 diabetes. With CGM, glucose readings are provided every 5 minutes, in addition to low and high glucose alerts and glucose trend information. The authors of this study aimed to determine the effectiveness of CGM in type 2 diabetic adults that receive multiple injections of insulin on a daily basis. In general, the results of the study suggested that type 2 diabetes patients using CGM have improved glycemic control. The main limitation of the study is that follow-up was restricted to 6 months. As a result, the long-term effects of CGM are unclear. Overall, the results of this study indicate that CGM could be beneficial for adults with type 2 diabetes who are receiving daily insulin injections.
Click to read the study, published in the Annals of Internal Medicine
Relevant Reading: The Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: In this randomized clinical trial, a total of 158 adult patients were divided into 2 arms: usual care or CGM. Patients had had type 2 diabetes for a median of 17 years and were receiving multiple daily injections of insulin. While the two patient cohorts did not differ significantly with respect to quality-of-life outcomes or CGM-measured hypoglycemia, the CGM group had improved glucose control. Specifically, the mean HbA1c levels in the intervention group decreased to 7.7%, compared to the control group where they only decreased to 8.0% at 24 weeks (adjusted difference in mean change, -0.3% [95% CI, -0.5% to 0.0%]; p = 0.022).
Image: CC/Wiki
©2017 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.