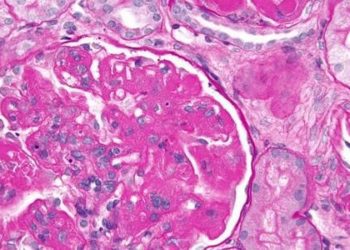
Dazukibart is effective in reducing disease activity in adults with refractory dermatomyositis
1. CDASI-A score at 12 weeks was significantly lower in dazukibart 600 mg versus placebo, suggesting reduced morbidity.
2. Treatment-related adverse events were comparable between all three groups.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Dermatomyositis is an autoimmune condition driven by type I interferon dysregulation. Current treatments fail to provide effective symptom control, highlighting the need for targeted therapies. This randomized controlled trial aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of dazukibart, a monoclonal antibody that neutralizes IFN-β, in adults with moderate-to-severe dermatomyositis. The primary outcome of this study was the change in Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index-Activity (CDASI-A) score at 12 weeks, while a key secondary outcome was safety. According to study results, dazukibart significantly reduced CDASI-A scores, demonstrating a pronounced improvement in disease activity. Although this study was well done, it was limited by a relatively small sample size.
Click to read the study in The Lancet
Relevant Reading: Trial of Intravenous Immune Globulin in Dermatomyositis
In-depth [randomized controlled trial]: Between Jan 23, 2018, and Feb 23, 2022, 125 patients were screened for eligibility across 25 university hospitals in Germany, Hungary, Poland, Spain, and the USA. Included were patients ≥ 18 years old with skin-predominant or muscle-predominant advanced dermatomyositis. Altogether, 75 patients (15 to dazukibart 150 mg, 37 to dazukibart 600 mg and 23 to placebo) were included in the final analysis. The primary outcome of CDASI-A score at 12 weeks was significantly lower in dazukibart 600 mg compared to placebo (mean change -19.2, 90% confidence interval [CI] -21.5 to -16.8, p<0.0001). The secondary outcome of safety revealed a similar incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events across groups (80% in dazukibart 150 mg, 81% in dazukibart 600 mg, and 78% in placebo). One death occurred in the dazukibart 600 mg group due to haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Overall, findings from this study suggest that dazukibart is a promising and well-tolerated option for advanced dermatomyositis.
Image: PD
©2025 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.

![2 Minute Medicine: Pharma Roundup: Price Hikes, Breakthrough Approvals, Legal Showdowns, Biotech Expansion, and Europe’s Pricing Debate [May 12nd, 2025]](https://www.2minutemedicine.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/ChatGPT-Image-May-12-2025-at-10_22_23-AM-350x250.png)