Integrated 2D/3D mammography improves breast cancer detection
Image: PD
1. Compared to 2D mammography alone, integrated 2D and 3D mammography facilitated detection of more breast cancers in asymptomatic women.
2. Less false positives occurred with integrated mammography than with conventional 2D mammography alone.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
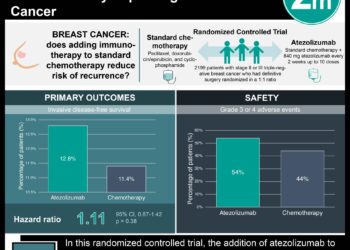
Study Rundown: This study found that integrated 2D and 3D mammography, or 2D mammography combined with digital breast tomosynthesis with 3D images, detected more breast cancers than 2D mammography alone and was associated with a lower incidence of false positive findings. These results are timely given recent investigations characterizing the problem of breast cancer overdiagnosis associated with population-level mammography screenings. Strengths of this investigation include a large sample size (n=7,292) and within-subject comparisons of mammography method that allowed each woman to serve as her own control. Future investigations might employ a randomized controlled design to evaluate the long-term effects of integrated mammography on morbidity and mortality.
Click to read the study in Lancet Oncology
Relevant Reading: Overview of the evidence on digital breast tomosynthesis in breast cancer detection
In-Depth [prospective comparative study]. This study assessed screening outcomes using integrated 2D and 3D mammography versus 2D mammography alone in a cohort of 7,292 asymptomatic Italian women at average risk for breast cancer (ages ≥48 years). Each participant received both 2D and 3D mammography. Outcomes included cancers detected, false positives, and incremental cancer detection.
Overall, integrated mammography yielded a detection rate of 8.1 per 1,000 screens (95% CI: 6.2-10.4) while 2D mammography alone provided a detection rate of 5.3 cancers per 1,000 screens (CI: 3.8-7.3, p<0.0001) such that the incremental improvement in cancer detection rate attributable to method was 2.7 cancers per 1,000 screens (CI: 1.7-4.2). False-positive findings were recorded in 2% (CI: 1.6-2.3) of patients with 2D mammography only and in 1% (CI: 0.8-1.3) of patients with integrated mammography (p<0.0001).
By Caroline Huang and Leah Hawkins
More from this author: One third of breast cancer survivors report pain 5-7 years after treatment, Varenicline reduces post-quit smoking relapses, Severe maternal childhood abuse associated with autism in offspring, 233 million women projected to lack modern contraceptives by 2015, Reminder intervention increases colorectal cancer screening rates, After-school program increases physical activity in overweight children, School-based therapy reduces asthma symptoms
© 2013 2minutemedicine.com. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without written consent from 2minutemedicine.com. Disclaimer: We present factual information directly from peer reviewed medical journals. No post should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2minutemedicine.com. PLEASE SEE A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IN YOUR AREA IF YOU SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE OF ANY SORT. Content is produced in accordance with fair use copyrights solely and strictly for the purpose of teaching, news and criticism. No benefit, monetary or otherwise, is realized by any participants or the owner of this domain.