Reminder intervention increases colorectal cancer screening rates
[tabs tab1=”2MM Rundown” tab2= “2MM Full Report”]
[tab]
Image: PD
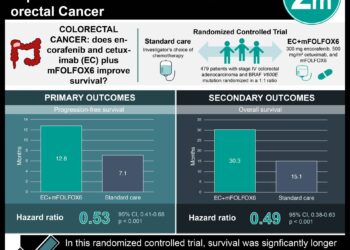
1. Among adults overdue for colorectal cancer screening, those who received reminder letters and mailed fecal occult blood test kits were twice as likely to adhere to screening guidelines.
2. Increases in screening among participants in the intervention groups were primary related to increased uptake of fecal occult blood testing; rates of completed colonoscopy were similar across groups.
Findings from this study indicate that automated reminder interventions increased annual colorectal cancer screening rates over a two-year period. The largest increase in screening rates occurred between usual care and the lowest intensity intervention, the automated mailings group. Increases in screening were driven by increased uptake of fecal occult blood testing in the intervention groups, with no effect on colonoscopy uptake.
Generalizability may be limited because the population was heavily white (80%), young (85% between 50-64 years), and inclined to pursue preventive care. Strengths include multiple levels of intervention intensity studied and large sample size (n=4,675). Future evaluation of screening interventions should examine long-term (>10-year) adherence to screening and should include cost considerations. Research on how adherence to screening guidelines (including both fecal occult blood tests and colonoscopies) affects the morbidity and mortality of colorectal cancers would provide a more complete view of intervention effectiveness.
Click to read the study in Annals of Internal Medicine
[/tab]
[tab]
Image: PD
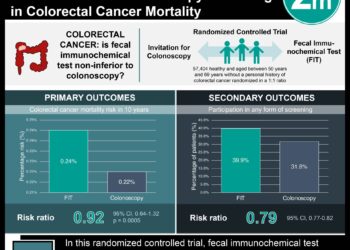
1. Among adults overdue for colorectal cancer screening, those who received reminder letters and mailed fecal occult blood test kits were twice as likely to adhere to screening guidelines.
2. Increases in screening among participants in the intervention groups were primary related to increased uptake of fecal occult blood testing; rates of completed colonoscopy were similar across groups.
This [randomized controlled effectiveness] trial assessed the effect of reminder interventions on colorectal cancer screening uptake among 4,675 adults ages 50-73 not currently following guidelines. Participants were randomized by age, clinic, and previous screening history to one of four groups: usual care, mailing reminders (usual care and automatically generated reminder letters and fecal occult blood test kit mailings), mailing and phone reminders (usual care, mailings, and reminder phone calls from a medical assistant), or intensive reminders (usual care, mailings, phone calls, and additional nurse support until patients completed or refused testing).
Compared to previously non-adherent adults receiving usual care, those receiving any intervention were more likely to adhere to screening guidelines (usual care: 26.3% (CI: 23.4-29.2), mailing reminders: 50.8% (CI: 47.3-54.4), mailing and phone reminders: 57.5% (CI: 54.5-60.6), and intensive reminders: 64.7% (CI: 62.5-67.0); all p<0.001). Increased screening uptake was likely related to increased fecal occult blood testing, which showed a dose-response effect by intensity of intervention: usual care: 3.9% (CI: 2.8-5.1); mailing reminders: 27.5% (CI: 24.9-30.0); mailing and phone reminders: 30.5% (CI: 27.9-33.2); and intensive reminders: 35.8% (CI: 33.1-38.6).
In sum: This study showed that automated reminder interventions increased annual colorectal cancer screening rates over a two-year period. The largest increase in screening rates occurred between usual care and the lowest intensity intervention, the automated mailings group. Increases in screening were driven by increased uptake of fecal occult blood testing in the intervention groups, with no effect on colonoscopy uptake.
Generalizability may be limited because the population was heavily white (80%), young (85% between 50-64 years), and inclined to pursue preventive care. Strengths include multiple levels of intervention intensity studied and large sample size (n=4,675). Future evaluation of screening interventions should examine long-term (>10-year) adherence to screening and should include cost considerations. Research on how adherence to screening guidelines (including both fecal occult blood tests and colonoscopies) affects the morbidity and mortality of colorectal cancers would provide a more complete view of intervention effectiveness.
Click to read the study in Annals of Internal Medicine
By Caroline Huang and Leah Hawkins
More from this author: After-school program increases physical activity in overweight children, School-based therapy reduces asthma symptoms, Ethical argument for opt-out approach to DNR status in terminally ill children, Positive response to alcohol ads in young adolescence associated with alcohol-related problems later
© 2013 2minutemedicine.com. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without written consent from 2minutemedicine.com. Disclaimer: We present factual information directly from peer reviewed medical journals. No post should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2minutemedicine.com. PLEASE SEE A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IN YOUR AREA IF YOU SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE OF ANY SORT. Content is produced in accordance with fair use copyrights solely and strictly for the purpose of teaching, news and criticism. No benefit, monetary or otherwise, is realized by any participants or the owner of this domain.
[/tab]
[/tabs]


![Pertussis immunity decreases after 5 DTaP doses [Researcher Comment]](https://www.2minutemedicine.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/03/9423_lores1-75x75.jpg)

