IV ferric carboxymaltose reduces risk of heart failure hospitalizations in patients with iron-deficiency and acute heart failure
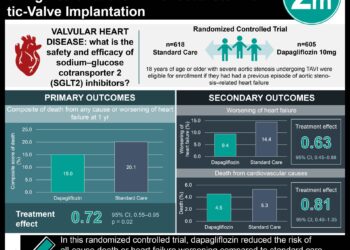
1. Treatment with IV ferric carboxymaltose reduced the risk of heart failure hospitalizations in patients with iron deficiency and acute heart failure with a left ventricular ejection fraction less than 50%.
2. IV ferric carboxymaltose was generally safe but had no significant effect on the risk of cardiovascular death compared to placebo.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Iron deficiency is a common comorbidity in patients with heart failure and is associated with increased risk of hospitalization and mortality. IV ferric carboxymaltose has previously been shown to improve symptoms and was associated with a lower rate of hospitalizations and cardiovascular mortality in patients with chronic heart failure. However, it is unclear if IV ferric carboxymaltose could have beneficial effects on patients admitted for acute heart failure where risk of mortality and re-hospitalization remains high. This randomized controlled trial included adults hospitalized for acute heart failure with concomitant iron deficiency. Patients were randomized at time of discharge to receive either IV ferric carboxymaltose or placebo for up to 24 weeks. Results suggested that treatment with ferric carboxymaltose reduced the risk of heart failure hospitalizations in patients with iron deficiency, left ventricular ejection fraction less than 50% and who had stabilized following admission with acute heart failure. Treatment with ferric carboxymaltose was generally safe but had no significant effect on the overall risk of cardiovascular death. Notably, the results of the trial may have been significantly impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic with regard to data collection and follow-up with a pre-COVID-19 sensitivity analysis demonstrating a significant benefit of ferric carboxymaltose on combined total heart failure hospitalizations and cardiovascular mortality. Additionally, the study design did not include patients assigned to receive oral iron supplementation and therefore it is unclear if the benefit seen extends to this group.
Click to read the study in The Lancet
Relevant Reading: Ferric Carboxymaltose in Patients with Heart Failure and Iron Deficiency
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: This randomized, double-blind, controlled trial conducted in 121 centers across Europe, South America and Singapore included adults aged ≥18 years hospitalized for acute heart failure with left ventricular ejection fraction less than 50%, and concomitant iron deficiency defined as serum ferritin less than 100 ng/mL or 100-299 ng/mL with transferrin saturation of less than 20%. Patients were randomly assigned to receive either IV ferric carboxymaltose or placebo with the first dose of treatment administered before discharge from hospital. Additional doses were given at weeks 6, 12, and 24 if iron deficiency persisted. The primary endpoint was a composite of total heart failure hospitalizations and cardiovascular mortality up to 52 weeks of follow-up.
A total of 1132 patients met the inclusion criteria between March 2017 and July 2019 and were assigned to receive either IV ferric carboxymaltose or placebo. A total of 293 primary events (57.2 per 100 patient years) occurred in the ferric carboxymaltose group compared to 372 (72.5 per 100 patient years) in the placebo group (rate ratio [RR] 0.79, 95% CI 0.62 to 1.01; p=0.059) falling short of the conventional 5% statistical significance. However, in the pre-COVID-19 sensitivity analysis, 274 primary events occurred in 228 patients in the ferric carboxymaltose group compared to 363 events in 550 patients in the placebo group (RR 0.75, 95% CI 0.59 to 0.96; p=0.024). Significantly fewer heart failure hospitalizations occurred in the ferric carboxymaltose group (217) compared to the 294 in the placebo group (RR 0.74, 95% CI 0.58 to 0.94; p=0.013). There was no difference in cardiovascular death between the two groups (14% in both the ferric carboxymaltose group and placebo group; Hazard Ratio [HR] 0.96, 95% CI 0.70 to 1.32; p=0.81).
Image: PD
©2020 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.