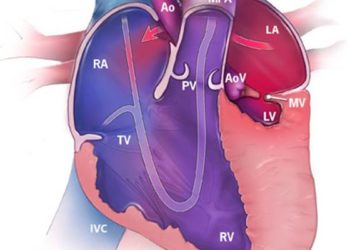
Ivabradine ineffective in stable coronary artery disease [SIGNIFY trial]
1. Ivabradine is an agent that lowers heart rate by specifically inhibiting the funny current.
2. In this trial, treating stable coronary artery disease patients without clinical heart failure with ivabradine did not significantly reduce mortality from cardiovascular causes. There was also no reduction in the rate of nonfatal myocardial infarctions compared to placebo.
3. The rate of adverse events were significantly higher in patients taking ivabradine when compared with placebo.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Reducing heart rate remains an important consideration in managing stable angina. Beta-blockers and calcium-channel blockers are common classes of medications used to reduce heart rate, though their use may be limited by adverse reactions or contraindications. Ivabradine was the first agent to be specifically developed to lower heart rate through inhibition of the funny current, with the benefit of having a minimal effect on blood pressure or left ventricular systolic function. In 2010, the SHIFT trial demonstrated that adding ivabradine to chronic heart failure management significantly reduced both hospitalization for worsening heart failure and mortality from heart failure. The purpose of the SIGNIFY trial was to determine if ivabradine would also be effective in treating patients with stable coronary artery disease (CAD) without clinical heart failure.
In summary, there was no significant difference between the ivabradine and placebo groups in terms of mortality from cardiovascular causes or nonfatal myocardial infarction. The rates of adverse events, however, were significantly higher in patients taking ivabradine (73.3% vs. 66.9%, P<0.001). Notably, the trial was supported by Servier, the manufacturer of ivabradine.
Click to read the study, published today in NEJM
Relevant Reading: Ivabradine and outcomes in chronic heart failure (SHIFT): A randomised placebo-controlled study
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: This randomized, placebo-controlled trial was conducted at 1,139 centers in 51 countries. Patients were eligible for the study if they were ≥55 years of age, had documented and treated stable CAD without evidence of clinical heart failure, in sinus rhythm and had resting heart rate ≥70 beats per minute on two electrocardiograms, and have at least one major or two minor prognostic factors. Patients were excluded from the trial if they had left ventricular dysfunction or an unstable cardiovascular condition. Included patients were randomized to receive ivabradine 7.5 mg twice daily or matching placebo. The primary endpoint was a composite of death from cardiovascular causes and nonfatal myocardial infarction.
A total of 19,102 patients were randomized for the trial. At three months, the mean heart rate was 60.7±9.0 beats per minute in the ivabradine group and 70.6±10.1 beats per minute in the placebo group and this difference was maintained for the duration of the study. There was no significant difference between the two groups in the rate of the primary endpoint (HR 1.08; 95%CI 0.96-1.20). Moreover, there were no significant differences between the two groups in either death from cardiovascular causes (HR 1.10; 95%CI 0.94-1.28) or the incidence of nonfatal myocardial infarction (HR 1.06; 95%CI 0.94-1.21). The rate of adverse events was significantly higher in the ivabradine group (73.3% vs. 66.9%, P<0.001), with bradycardia being the most common type (18.0% vs. 2.3%, P<0.001).
Image: CC/Wiki
©2012-2014 2minutemedicine.com. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2minutemedicine.com. Disclaimer: We present factual information directly from peer reviewed medical journals. No post should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors, editors, staff or by 2minutemedicine.com. PLEASE SEE A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IN YOUR AREA IF YOU SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE OF ANY SORT.



![2MM: AI Roundup- AI Cancer Test, Smarter Hospitals, Faster Drug Discovery, and Mental Health Tech [May 2nd, 2025]](https://www.2minutemedicine.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/Untitled-design-350x250.png)

![Novel biodegradable sirolimus-eluting stents non-inferior to durable everolimus-eluting stents [BIOSCIENCE trial]](https://www.2minutemedicine.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/Taxus_stent_FDA-e1607803635904-75x75.jpg)

