Mesenchymal precursor cell transplant did not improve weaning from device support in LVAD patients
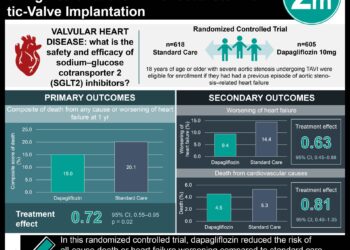
1. In this randomized controlled trial, the injection of mesenchymal precursor cells into the myocardium of patients undergoing a Left Ventricular Assist Device (LVAD) implant did not increase successful temporary weaning from device support.
2. LV Ejection Fractions (LVEFs) and quality of life scores were similar between groups.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Implantation of Left Ventricular Assist Devices (LVADs) is a key surgical therapy for advanced heart failure patients unresponsive to medical therapy. Injection of mesenchymal precursor cells (MPCs) is a promising adjuvant therapy that may promote cardiac recovery through suppression of inflammatory cytokines that can incite infection, bleeding, and thrombosis. In this randomized controlled trial, injection of MPCs did not improve LV recovery as determined by proportion of successful LVAD weans over 6 months. Similarly, LV Ejection Fractions (LVEFs) and quality of life scores were similar between groups.
Injection of MPCs may not have been effective for this condition for a variety of reasons, with one such reason being that cell delivery through direct transepicardial injection may result in significant cell loss and low rates of retention. The study’s conclusion is further limited by its enrollment of a wide spectrum of patients receiving 1 of 2 LVAD types, which may have increased variability in such a small trial.
Click to read the study, published today in JAMA
Click to read an accompanying editor’s note in JAMA
Relevant Reading: Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Cardiology
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: There were 159 patients with advanced heart failure from 9 North American centers who were hospitalized for a clinically indicated LVAD as bridge to heart failure or destination therapy for non-transplant candidates. Patients were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to an intramyocardial injection of 150 million MPCs or cryoprotective medium alone. Intramyocardial injections were performed at time of LVAD implant. All patients were followed for up to 12 months after randomization or until heart transplant. End points were evaluated at 2, 4, 6, 9, and 12 months. The primary endpoint was proportion of successful temporary weans (>= 30 minutes) out of 3 assessments (2, 4, and 6 months) from full to minimal LVAD support over 6 months. Secondary end points included 3 echocardiographic assessments timed to 3 stages of the weaning process: before full LVAD support was withdrawn, 15 minutes into weaning, and immediately following 6-minute walk test. Echocardiographic measurements included LVEF, LV dimensions, and right ventricular function. Other end points included survival, anti-HLA antibody sensitization and transplant, quality of life, and adverse events. Below the 80% threshold for a positive signal, MPCs increased likelihood of successful temporary weans from LVAD support of 3 planned assessments over 6 months at 69%. The mean proportion of successful weans over 6 months was 61% in the MPC group and 58% in the control group (rate ratio for wean success rate 1.08; CI95 0.83 to 1.41). Over 6 months, LVEFs were not significantly different between groups (difference in slopes 0.22; CI95 -0.26 to 0.70). Quality-of-life scores were not significantly different between groups (p > 0.05).
Image: PD
©2019 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.