Nucleoside-modified mRNA influenza vaccine more effective than standard shot in adults
1. A nucleoside-modified mRNA (modRNA) influenza vaccine showed greater protection against influenza-like illness compared to a standard inactivated vaccine in adults.
2. The modRNA vaccine triggered stronger immune responses to influenza A strains, while immune response to influenza B strains was less robust.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
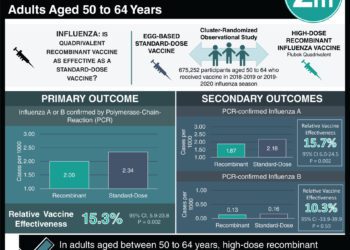
Study Rundown: Influenza continues to represent a large burden to the healthcare system, affecting millions of people and causing hundreds of thousands of hospitalizations annually. While vaccination prevents a substantial number of influenza-related illnesses, overall effectiveness against influenza remains suboptimal. Nucleoside-modified messenger RNA (modRNA)–based vaccines have several advantages over traditional egg-based vaccines, including direct matching to the targeted viral strain and the elimination of egg-adaptive mutations which may reduce effectiveness in humans. This randomized controlled trial evaluated the efficacy, immunogenicity, and safety of a quadrivalent nucleoside-modified mRNA influenza vaccine compared to a licensed inactivated vaccine (FLUZONE) during the 2022–2023 flu season across the U.S., South Africa, and the Philippines. The trial involved nearly twenty-thousand adults and demonstrated that the modRNA vaccine had significantly greater efficacy against laboratory-confirmed influenza-like illness compared to control. Immunogenicity analysis demonstrated noninferiority for influenza A strains but not for B strains, as measured by hemagglutination inhibition (HAI) titers and seroconversion rates. Notably, modRNA recipients showed stronger T-cell responses, especially CD8+ activation, which persisted up to 6months post-vaccination. Reactogenicity events such as pain, fatigue, headache, and fever were more common with modRNA but were mostly mild. Serious adverse events were rare and comparable between groups, with no cases of confirmed myocarditis or pericarditis. This study was limited by a lack of analysis regarding absolute vaccine efficacy, a single-season design, and the insufficient inclusion of populations outside of the United States. Nonetheless, these results suggest that a modRNA vaccine was more effective in preventing first-time influenza infection in adults compared to the standard inactivated vaccine.
Click to read the study in NEJM
Relevant Reading: A Phase 1/2 Randomized Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, and Immunogenicity of Nucleoside-Modified Messenger RNA Influenza Vaccines in Healthy Adults
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: This multicenter, randomized, observer-blinded phase 3 trial compared a quadrivalent nucleoside-modified mRNA (modRNA) influenza vaccine with a licensed inactivated influenza vaccine in healthy adults aged 18 to 64 years. Participants were enrolled across the United States, South Africa, and the Philippines during the 2022–2023 influenza season. A total of 18,476 participants were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive either the modRNA vaccine or the control vaccine. The trial aimed to assess efficacy against lab-confirmed influenza-like illness, as well as immunogenicity and safety outcomes. The modRNA vaccine showed greater efficacy in preventing laboratory-confirmed influenza-like illness, meeting both noninferiority and superiority thresholds. Most confirmed influenza cases were due to A/H3N2 and A/H1N1 strains, with very few B strain cases detected during the season. Immunogenicity was assessed in a subset of around one-fifth of participants, with blood samples collected before and after vaccination. The modRNA vaccine induced stronger antibody responses to influenza A strains, but did not achieve noninferiority for B strains. Additionally, participants who received the modRNA vaccine had increased activation of both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, with higher interferon-γ expression, suggesting enhanced cell-mediated immunity. Local and systemic side effects were more commonly reported in the modRNA group, though most were mild or moderate in intensity and resolved quickly. Serious adverse events were rare and occurred at similar rates in both groups. No new safety concerns emerged during the 6-month follow-up, and there were no confirmed cases of myocarditis or pericarditis. This trial demonstrates that a modRNA influenza vaccine can offer superior protection compared to a standard inactivated vaccine in healthy adults, particularly against circulating influenza A strains, and supports further development of mRNA-based vaccines for seasonal influenza prevention.
Image: PD
©2025 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.