Polypharmacy in non-care home residents strongly associated with higher rates of severe COVID-19
1. Polypharmacy in non-care home residents was strongly associated with higher rates of severe COVID-19.
Evidence Rating Level: 3 (Average)
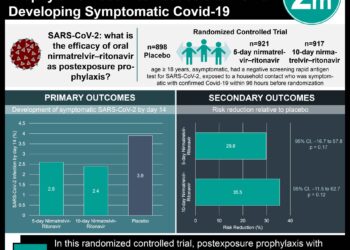
Resistant hypertension, which is uncontrolled despite maximal medical therapy, affects up to 10% of patients diagnosed with hypertension. Renal artery denervation has been demonstrated in a number of smaller, nonrandomized and/or unblinded studies to significantly reduce blood pressure in patients with resistant hypertension. In ongoing discussions about medication use that increased risk of experiencing severe disease from COVID-19, drugs acting on the renin-angiotensin system as well as those associated with an increased risk of community-acquired pneumonia were suggested. A recent review published a list of 17 widely prescribed drug classes associated with increased pneumonia risk, described as “medications compromising COVID”. An initial analysis of REACT-SCOT reported a strong association of severe COVID-19 with the dispensing of at least one prescription in the last year; this study aimed to investigate which drug classes may be responsible for this association. In this randomized controlled, pharmaceutical-sponsored trial, 535 patients were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to receive catheter-based radiofrequency renal artery denervation or a sham procedure (renal angiography only) to study the effect on participants’ office systolic blood pressure at 6 months compared to their baseline, with a superiority margin of 5mmHg. In this matched case-control study, all 4251 severe cases of COVID-19 in Scotland were matched to 36 378 controls from the Community Health Index database for age, sex, and same primary care practice. Records from hospital discharges since 2015 and prescriptions issued within the last 240 days were analysed. Results showed a strong association between the rate of severe COVID-19 and the number of classes of non-cardiovascular drugs dispensed. This association was restricted to patients who were not care home residents, with a rate ratio of 10.89 (95% CI 7.7-13.3) between COVID-19 and dispensing of 12 or more drug classes over those with no prescriptions; this association was also stronger in those under 75 years of age and/or without any conditions known to confer vulnerability to COVID-19. Interestingly, this trend decreased with the number of cardiovascular drug classes dispensed. All 17 drug classes listed as “medications compromising COVID” were associated with an increased risk of COVID-19. A multivariable regression showed the strongest independent associations were with antipsychotic drugs (RR 4.18 (95% CI 3.42-4.11), proton pump inhibitors (at 2 defined daily doses/day, RR 2.2 (95% CI 1.72-2.83)), and opioid analgesics (for 50 mg morphine equivalents/day, RR 3.66 (2.68-5.01)), as well as with gabapentinoids and antihistamines.These associations persisted after adjustment for covariates and were stronger with more recent exposure. To note, data on severity of comorbidities of these patients and no morbidity data from primary care, such as on health behaviours like smoking, could be collected. Nonetheless, these results found associations with severe COVID-19 and polypharmacy, namely drugs likely to cause sedation, respiratory depression, dyskinesias, anticholinergic effects, and/or affect the gastrointestinal tract. Guidance on reducing overprescribing and generally inappropriate pharmacy should be reinforced.
Click to read the study in BMC Medicine
Image: PD
©2020 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.