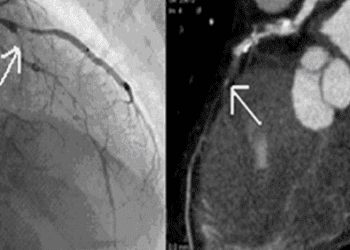
Reduced mortality with culprit-lesion-only percutaneous coronary intervention for acute myocardial infarction with cardiogenic shock
1. In patients with acute myocardial infarction (MI) with cardiogenic shock and multivessel coronary disease, culprit-lesion-only percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) had a lower risk of 30-day mortality compared to multivessel PCI.
2. There was no evidence that rates of renal-replacement therapy, bleeding, recurrent myocardial infarction, or stroke were different between the treatment arms.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Cardiogenic shock is a deadly sequela of MI, with most patients presenting with multivessel coronary disease. PCI of the culprit vessel reduces mortality in cardiogenic shock, but it is unknown whether concurrent PCI of nonculprit vessels further improves outcomes. This randomized controlled trial compared these two revascularization strategies in patients with acute myocardial infarction with cardiogenic shock and multivessel coronary disease. The primary outcome was a composite of 30-day death or requirement of renal-replacement therapy. Compared to the multivessel PCI treatment arm, participants in the culprit-lesion-only group had a significantly lower risk of the primary outcome and of mortality. This effect was consistent across multiple subgroups. There was no evidence that risks of renal-replacement therapy, bleeding, recurrent myocardial infarction, or stroke were different between the treatment arms. Overall, this trial provides strong evidence that culprit-vessel-only PCI is a superior treatment strategy to multivessel PCI in the acute treatment of cardiogenic shock secondary to MI.
Strengths of this study include the randomized study design with recruitment from multiple sites, and inclusion of patients with chronic total occlusions who have been excluded from previous trials. Limitations include lack of blinding and an event rate and effect size that were mildly lower than expected, reducing the study power.
Click to read the study in NEJM
Relevant Reading: Early Revascularization and Long-term Survival in Cardiogenic Shock Complicating Acute Myocardial Infarction
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: This European multicenter randomized controlled trial enrolled 351 patients in the culprit-lesion-only PCI group and 355 patients in the multivessel PCI group. Inclusion criteria included acute MI with cardiogenic shock, an identifiable culprit lesion, and over 70% stenosis in at least two major vessels. Patients who were resuscitated for over 30 minutes, or who had an indication for urgent coronary-artery bypass grafting were excluded. The primary endpoint was a composite of 30-day death or requirement of renal-replacement therapy; these outcomes were also assessed independently as secondary endpoints. Other secondary endpoints included recurrent MI, repeat revascularization, and rehospitalization for congestive heart failure. Key safety endpoints were rates of bleeding and stroke.
The rate of the primary endpoint was 45.9% in the culprit-lesion-only PCI group, and 55.4% in the multivessel PCI group (relative risk [RR], 0.83; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.71 to 0.96; p=0.01). Risk of death was also lower in the culprit-lesion PCI group (43.3%) compared to the multivessel group (51.6%) (RR=0.84; 95%CI, 0.72 to 0.98; p=0.03). Risk of renal-replacement therapy was similar between the culprit-lesion and multivessel groups (11.6% vs 16.4%; RR=0.71; 95% CI, 0.49 to 1.03; p=0.07). Rates of recurrent MI, rehospitalization for congestive heart failure, bleeding, and stroke did not differ significantly between the treatment arms (p>0.05).
Image: PD
©2017 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.