The VADT-F trial: major cardiovascular events or death are not reduced in diabetics with intensive glucose control therapy
1. In a 15-year observational cohort study of type 2 diabetics treated with intensive compared to standard glucose control therapy the risk of major cardiovascular event or death was similar between both treatment groups.
2. There was no reported difference in health-related quality of life scores between the intensive and standard therapy groups.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Associations have been found in observational studies between high blood glucose levels and adverse events in diabetic patients. Associations have been more supported between microvascular adverse events and poor glucose control, while macrovascular outcomes such as cardiovascular events and their association with blood glucose control is less well established. The VADT-F study examined long-term glucose control therapy with data reaching 15-years, including 10-years of observational study after an initial 6-years of intensive glucose control therapy. The primary outcome of composite major cardiovascular events, including death, after 15 years were not lower in the intensive therapy group compared to the standard group.
This study provides long-term observational data to suggest intensive glucose control therapy does not significantly reduced the risk of major cardiovascular events. Its strengths include it’s long-term follow-up of both adverse events and glucose control. The study’s inclusion of mostly elderly men limits it’s generalizability.
Click to read the study in NEJM
Relevant Reading: Long-term benefits of intensive glucose control for preventing end-stage kidney disease: ADVANCE-ON
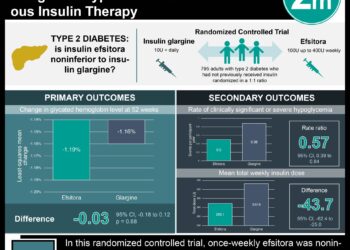
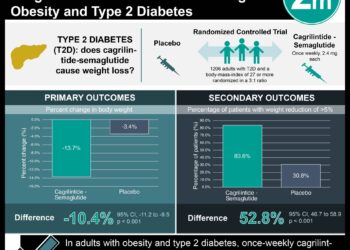
In-Depth [prospective cohort]: This prospective cohort study initially included 1791 military veterans with type 2 diabetes mellitus who were randomized to either intensive or standard glucose control therapy. Patients in the intensive group (n=892) had a treatment goal of normal glycated hemoglobin levels, while those in the standard group (n=899) had a glycated hemoglobin goal of between 8-9%. Participants were in these therapy groups for 5.6 years, and follow-up was performed on alive patients through national electronic medical registries. At a mean follow-up period of 13.6 years, the primary outcome of composite major cardiovascular events or death was no significantly different between the intensive and standard therapy groups (hazard ratio, 0.91; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.78 to 1.06; P = 0.23). There were no significant differences in rates of major diabetic events (hazard ratio, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.78 to 1.04) or death from cardiovascular causes (hazard ratio, 0.94; 95% CI, 0.73 to 1.20). Mean scores for health-related quality of life and rates of hospitalization were also similar between the two groups. After the active phase of the study had finished, glycated hemoglobin levels in the intensive therapy group gradually returned to approximately the same level as those of patients in the standard therapy group.
Image: PD
©2019 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc