#VisualAbstract: Catheter ablation reduces rates of persistent atrial fibrillation and atrial tachyarrhythmia
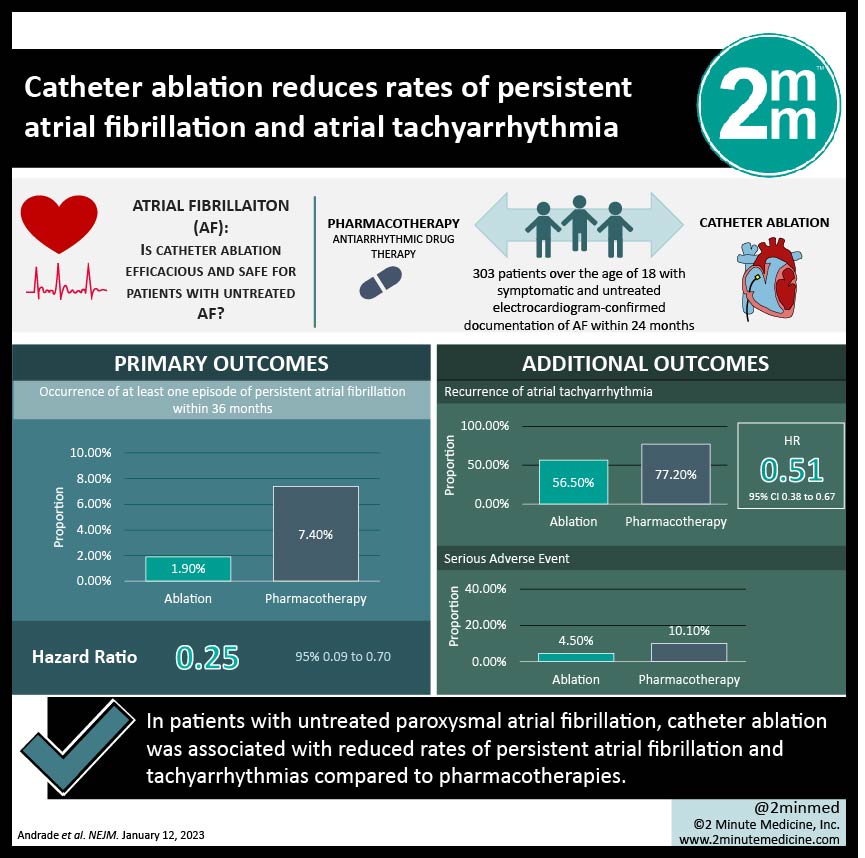
1. In patients with untreated paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, catheter ablation was associated with reduced rates of persistent atrial fibrillation and tachyarrhythmias compared to pharmacotherapies.
2. Catheter ablation was also associated with a lower rate of serious adverse events when compared to antiarrhythmic pharmacotherapy.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Atrial fibrillation is an irregular and fast heart rhythm that can be progressive and chronic. It is associated with a range of complications, such as blood clots and heart failure. Currently, the optimum strategy for treating atrial fibrillation with regard to establishing control of ventricular rhythm is unclear. The main techniques are catheter ablation and pharmacologic control through antiarrhythmic medications. This study was a multi-center randomized trial conducted in Canada investigating the effectiveness and safety profile of single ablation technology against antiarrhythmic pharmacotherapy. Patients with early paroxysmal atrial fibrillation who are symptomatic and have never previously been treated were included. This study found that catheter ablation was more effective than pharmacotherapy at reducing rates of at least one episode of persistent atrial fibrillation and rates of recurrent tachyarrhythmias after the start of the trial. It was also associated with an improved safety profile in terms of a lower proportion of patients experiencing a serious adverse event. Although, this study is limited by significant crossing over of treatment arms (unidirectionally from pharmacotherapy to catheter ablation). Further, results are not generalizable beyond the specific anti-arrhythmic medications and ablation techniques which were utilized.
Click to read the study in NEJM
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: This study was a multicenter, randomized controlled trial involving 18 study sites in Canada which investigated the efficacy and safety outcomes of cryoballoon ablation compared to anti-arrhythmic pharmacotherapy in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Persons older than 18 years old who were symptomatic and not previously treated were included if they had electrocardiogram-confirmed documentation of atrial fibrillation within the previous 24 months. All patients included were implanted with a cardiac monitor to detect cardiac cycle activity. After the application of selection criteria, 303 patients were randomly assigned to receive ablation (n=154) or pharmacotherapy (n=149). The primary outcome of interest was the occurrence of at least one episode of persistent atrial fibrillation within 36 months. Additional outcomes of interest included recurrence of atrial tachyarrhythmia, Atrial Fibrillation Effect on Quality-of-Life survey (AFEQT) score, and adverse events. Results of the primary analysis found that patients receiving pharmacotherapy were more likely to have at least one episode of persistent atrial fibrillation than patients receiving ablation (Hazard Ratio [HR], 0.25; 95% Confidence Interval [CI], 0.09 to 0.70), and more likely to have recurrent atrial tachyarrhythmia (HR, 0.51; 95% CI 0.38 to 0.67). At the final follow-up, 23.5% of patients in the pharmacotherapy group (n=35) and 11.0% of patients in the ablation group (n=17) had experienced a serious adverse effect. This study supports catheter ablation as an initial mechanism of rhythm control for paroxysmal symptomatic atrial fibrillation not previously treated.
©2023 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.