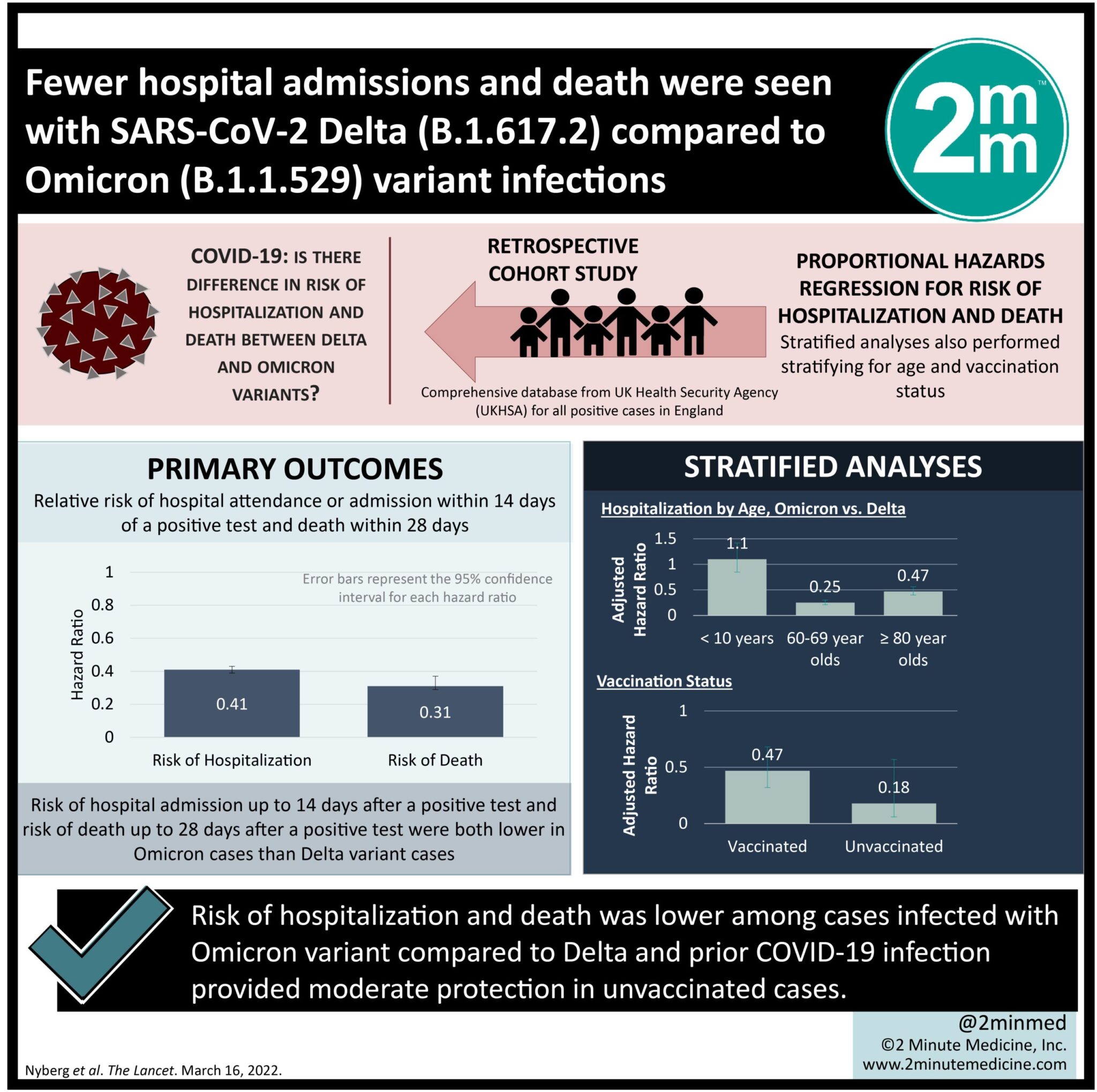
#VisualAbstract: Fewer hospital admissions and death were seen with SARS-CoV-2 Delta (B.1.617.2) compared to Omicron (B.1.1.529) variant infections
1. The risk of hospitalization and death was lower among cases infected with Omicron variant compared to Delta.
2. In unvaccinated cases, prior COVID-19 infection provided moderate protection.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Delta (B.1.617.2) and omicron (B.1.1.529) are two major identified variants of the COVID-19 pandemic. This retrospective cohort study aimed to characterize the difference in severity between the two variants for different age groups. Using a comprehensive database of individual patient data for all positive cases in England, this study compiled data of all laboratory-confirmed delta and omicron infections before January 24, 2022. Risk of hospitalization and death was shown to be lower in omicron cases versus delta cases. Compared to vaccinated cases, unvaccinated cases showed a greater risk reduction for hospitalization in the delta variant cases. This may suggest a reduction in vaccination effectiveness for the omicron variant compared to delta. Secondary outcomes measured by this study included severity by age, which showed that the greatest variation between delta and omicron was seen in the older population. Additionally, prior infection was shown to reduce the risk of hospitalization and death comparable to receiving one dose of an mRNA vaccine. Limitations of this study include the inability to control for testing rates between delta and omicron variants. Nonetheless, this study was a large-scale analysis which provides important information regarding the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic and further demonstrates the need for detailed surveillance.
Click to read the study in the Lancet
Relevant Reading: Early assessment of the clinical severity of the SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant in South Africa: a data linkage study
In-Depth [retrospective cohort study]: This retrospective cohort study used data reported to the UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) for all positive cases in England. Individuals included in the study had laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection of either S-gene positive (delta) or S-gene negative (omicron) variants before Dec 30, 2021. After this date, the prevalence of S-gene positive omicron (BA.2) lineage was increasing, thus making S-gene positivity less predictive of delta. 1 516 702 of the 4 135 347 (37%) of the identified SARS-CoV-2 cases met the criteria for inclusion with 448 843 delta and 1 067 859 omicron. 1.3% of delta cases and 9.6% of omicron cases were re-infections of individuals who had tested positive 90 days prior. Risk of hospital admission up to 14 days after a positive test was lower in omicron cases (Hazard ratio [HR] 0.41, 95% CI 0.39-0.43), as well as risk of death up to 28 days after a positive test (HR 0.31, 0.29-0.37). When stratifying for age, the HR was 1.10 for admission in individuals younger than 10 and substantially below 1 when looking at older age groups. When analyzing only unvaccinated cases, the reduction in risk of hospitalization between delta and omicron was greater (HR 0.30, 0.28-0.32). Additionally, reduction in risk of hospitalization between the vaccinated versus unvaccinated was greater for delta than omicron cases. Past infections were shown to reduce the risk of hospitalization (HR 0.55, 0.48-0.63) and death (HR 0.18, 0.06-0.57) in the unvaccinated.
©2022 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.