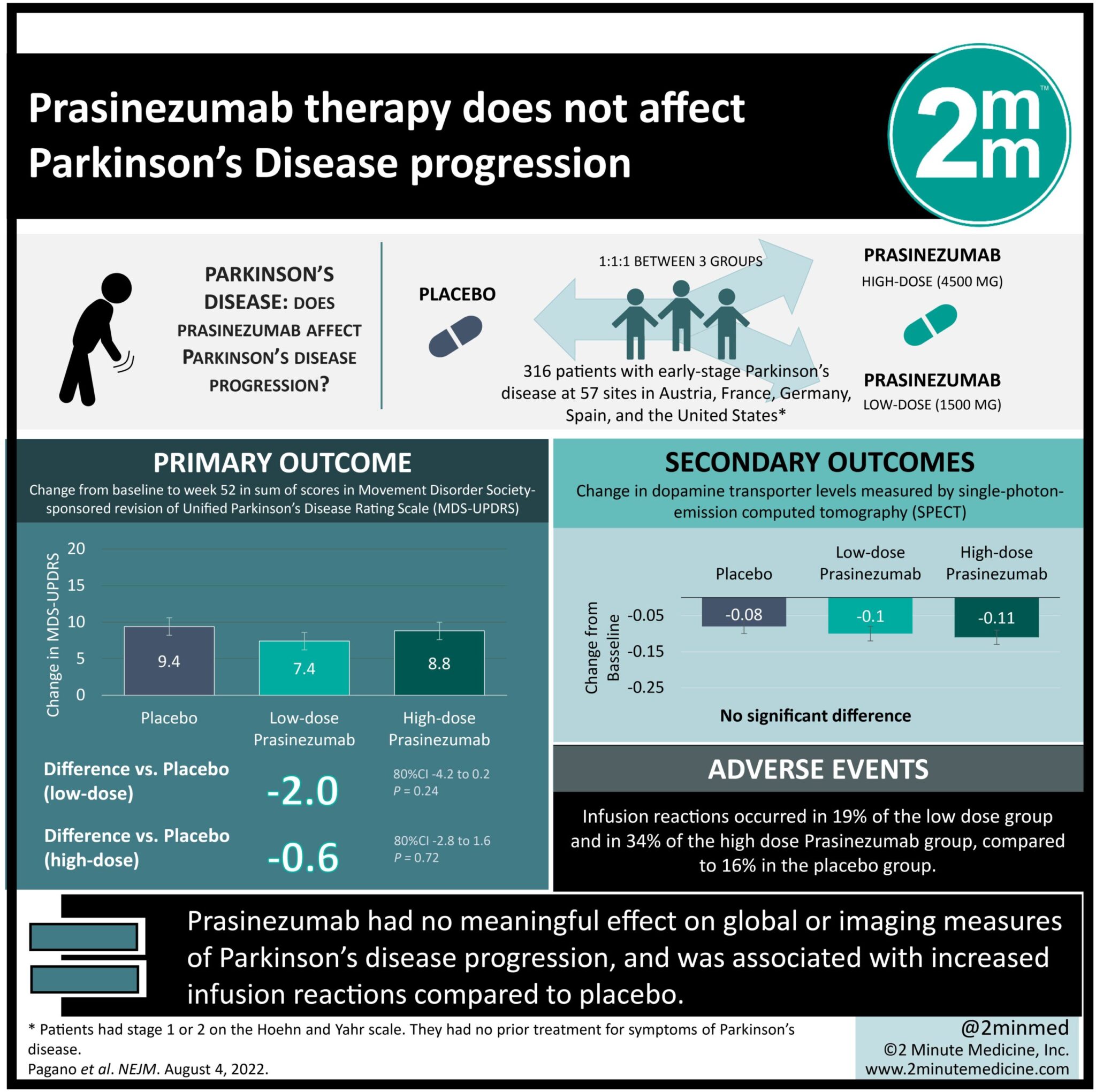
#VisualAbstract: Prasinezumab therapy does not affect Parkinson’s Disease progression
1. Prasinezumab had no meaningful effect on global or imaging measures of Parkinson’s disease progression.
2. Prasinezumab therapy was associated with increased infusion reactions compared to placebo.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Aggregated a-synuclein is a main factor in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Prasinezumab was designed as a monoclonal antibody to bind aggregated a-synuclein at the C-terminal selectively. In phase one trials, Prasinezumab has been demonstrated to show brain penetration. Further, it has resulted in dose-dependent reductions from baseline free serum a-synuclein levels. However, there is a knowledge gap in understanding the efficacy and safety of low dose (1500mg) and high dose (4500 mg) Prasinezumab in patients with early-stage Parkinson’s disease. Overall, the present study found that treatment with Prasinezumab had no meaningful effect on global clinical or imaging measures of Parkinson’s disease progression. This study was limited by the planned censoring of data from participants when they started treatment for symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. The trial population was also not representative of the wider population of persons with Parkinson’s disease, as non-White, non-United States, and non-European populations were underrepresented. Nevertheless, the study’s findings are significant, as they demonstrate that Prasinezumab has no clinically meaningful effect on early-stage Parkinson’s disease progression.
Click to read the study in NEJM
Relevant Reading: Randomized Trial of Focused Ultrasound Subthalamotomy for Parkinson’s Disease
In-Depth [randomized control trial]: This randomized phase two trial assigned participants with early-stage Parkinson’s disease in a 1:1:1 ratio to receive either intravenous placebo, low-dose Prasinezumab, or high-dose Prasinezumab every four weeks for 52 weeks. Patients who had early-stage Parkinson’s disease, findings on dopamine transporter imaging with SPECT that were consistent with Parkinson’s, and no previous treatment for symptoms of Parkinson’s disease were eligible for the study. The primary outcome measure was the change from baseline to week 52 in the sum of scores of the Movement Disorder Society-sponsored revision of the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS), with higher scores indicating greater impairment. Outcomes in the primary analysis were assessed via pairwise comparison and efficacy analyses. Based on the primary analysis, the mean changes in the MDS-UPDRS scores were 9.4+/-1.2 in the placebo group, 7.4+/-1.2 in the low-dose Prasinezumab group (difference versus placebo, -2.0; 80% Confidence Interval [CI], -4.2 to 0.2), and 8.8+/-1.2 in the high dose Prasinezumab group (difference versus placebo, -0.6; 80% CI -2.8 to 1.6). There was no significant difference between the Prasinezumab treatment groups and the placebo group in dopamine transporter levels on SPECT. Moreover, infusion reactions occurred in 19% of the low dose group and in 34% of the high dose Prasinezumab group. Overall, this study demonstrates that Prasinezumab has no significant nor clinically meaningful effect on global or imaging measures of Parkinson’s disease progression, suggesting it is not an effective therapy for preventing or slowing the progression of early-stage Parkinson’s disease.
©2022 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.



![ABCD2 Score: Predicting Early Stroke Risk After Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) [Classics Series]](https://www.2minutemedicine.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/05/web-cover-classics-with-logo-medicine-BW-small-jpg-75x75.jpg)



