#VisualAbstract: Second-line immunosuppression associated with worse outcomes for immune-related adverse events in melanoma
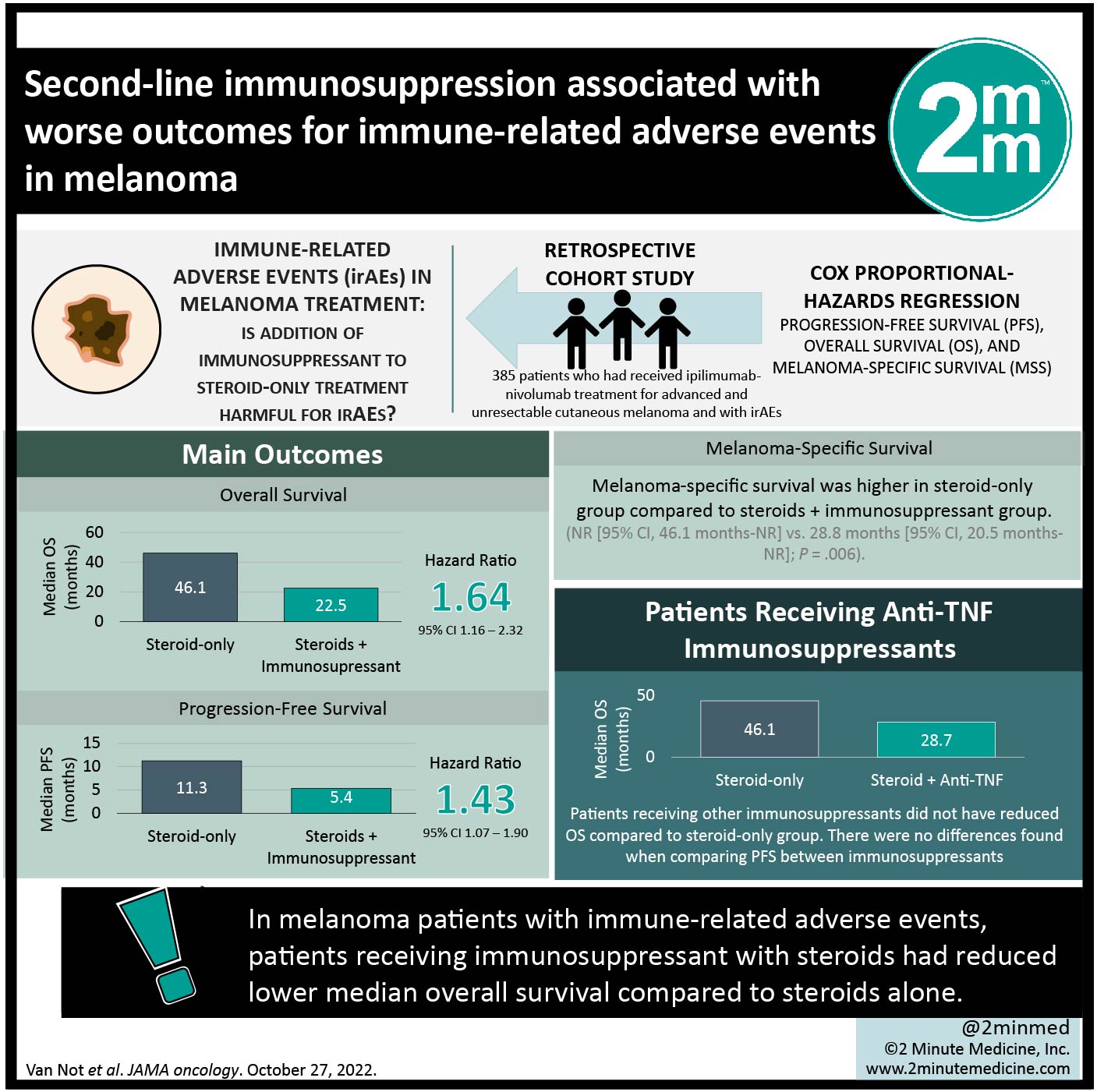 1. Median overall survival was longer in patients receiving steroid-only treatment for adverse events associated with immune response.
1. Median overall survival was longer in patients receiving steroid-only treatment for adverse events associated with immune response.
2. Patients receiving steroids plus any immunosuppressant for treatment of immune-related adverse events had reduced median progression free survival.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Study Rundown: Immune-related adverse events (irAEs) are hypothesized to arise secondary to immune activation during treatment of cancers like melanoma with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). This study investigated the association of adverse event management with both overall and progression free survival (OS and PFS, respectively) in patients receiving ipilimumab-nivolumab combination therapy. It was found that median OS was longer in patients who only had steroids as treatment for their irAEs, when compared to patients receiving immunosuppressants as well. Similarly, patients taking anti-TNF immunosuppressants in addition to steroid treatment had reduced OS compared to steroids-only treatment, but patients receiving any other immunosuppressants did not. The median PFS for patients on steroid-only treatment was greater than the median PFS of patients receiving steroids and second line immunosuppressants. Median PFS on either immunosuppressant was reduced, compared to steroid-only treatment. There were no differences found when comparing PFS between immunosuppressants. Limitations to this study include the fact that information regarding which immunosuppressant was provided to specific irAEs was absent from the data. Additionally, information about immunosuppressant dose and duration was not available from the data, suggesting that a causal association cannot be inferred between outcome and immunosuppressants. Overall, the results from this study revealed that patients receiving only steroids for irAEs fared better than those who received steroids plus other immunosuppressant therapeutic treatment.
Click to read the study in JAMA Oncology
Relevant Reading: TNF in the era of immune checkpoint inhibitors: friend or foe?
In-Depth [retrospective cohort]: This study utilized a database to enroll 385 patients who had received ipilimumab-nivolumab treatment for advanced and unresectable cutaneous melanoma and stratified them based on how their AEs were managed (steroids only vs. steroids with 2nd-line immunosuppressants (either anti-TNF or other). The most frequently noted AEs were colitis (146 patients) and hepatitis (139 patients). Median OS was longer in patients who received only steroids (46.1 months (95% CI, 39.0-not reached (NR)) as compared with those on steroids and immunosuppressant (22.5 months 95% CI, 36.5 months-NR; HR, 1.64; 95% CI, 1.16-2.32). This remained true when comparing to anti-TNF immunosuppressants as well (28.7 months, 95% CI, 12.2 months-NR; HR, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.07-2.46), but not when comparing to other immunosuppressants (22.4 months; 95% CI, 13.2 months-NR; HR, 1.59; 95% CI, 0.95-2.65). The median PFS was longer for patients receiving only steroids for management of their AEs (11.3 months, 95% confidence interval (CI), 9.6-19.5 months) as compared to those receiving steroids and either second-line immunosuppressant (5.4 months, 95% CI, 4.5-12.4 months; hazard ratio (HR), 1.43; 95% CI, 1.07-1.90). Similarly, patients on steroid plus anti-TNF or other immunosuppressant had shorter median PFS (5.4 months (95% CI, 4.7-13.1 months) and 4.3 months (95% CI, 2.5-13.2 months), respectively). There was no significant difference in PFS between immunosuppressant groups.
©2022 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.