Closed-loop insulin delivery systems may improve glycemic outcomes compared to sensor-augmented pumps
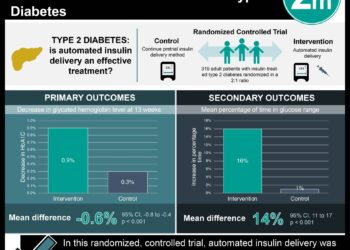
1. In this randomized controlled trial, patients with type 1 diabetes who used a closed-loop system spent a greater percentage of time in a target glycemic range compared to those who used a sensor-augmented insulin pump.
2. The closed-loop system was effective in reducing glycated hemoglobin level as well as time spent in both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Insulin delivery systems are valuable in the management of type 1 diabetes, but American Diabetes Association glycemic targets remain difficult to meet consistently in a majority of patients. Closed-loop systems that automate both blood glucose monitoring and insulin administration hold the potential to dramatically improve patient health outcomes, but their safety and efficacy remain to be tested in randomized trials. This 6-month study compared a third-generation closed-loop system with a sensor-augmented pump, finding that the closed-loop system was more effective in maintaining a blood glucose level within the target range at all times of day. Notably, the closed-loop system demonstrated superior mitigation of the dawn phenomenon, better controlling blood glucose in the morning hours. Patients in the treatment group also exhibited a decreased glycated hemoglobin level but experienced significantly more adverse events versus control. Strengths of the study included complete patient retention, high adherence, and substantial diversity across a broad range of characteristics. One major limitation was that the insulin pumps used by the control group lacked the ability to suspend infusion upon predicted hypoglycemia. This disparity could have greatly affected outcomes, thereby diminishing applicability of study findings.
Click here to read the study in NEJM
Relevant Reading: The Hybrid Closed-Loop System: Evolution and Practical Applications
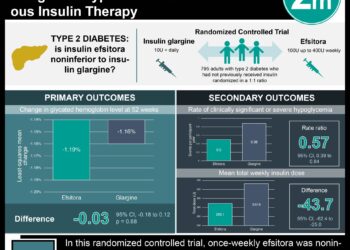
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: In this unblinded, multicenter, parallel-group trial, 168 patients between the ages of 14 and 71 were randomly assigned to the closed-loop group or the control group in a 2:1 ratio. Baseline characteristics including age, sex, body mass index, duration of diabetes, means of insulin administration, and glycated hemoglobin level were similar between groups. The primary outcome, the mean percentage of time with glucose levels within the target range of 70-180 mg/deciliter, increased from 61% to 71% in the treatment group but remained stagnant at 59% in the control group (mean difference [closed loop minus control], 11 percentage points; 95% confidence interval [CI], 9 to 14; P<0.001). The closed-loop system demonstrated greater efficacy in preventing hyperglycemia (mean difference in percentage of time, -10; 95% CI, −13 to −8; P<0.001) than hypoglycemia (mean difference, -.88; 95% CI, −1.19 to −0.57; P<0.001). The between-group difference in mean glucose level was greatest at 5 a.m. and 6 a.m. (139 mg/deciliter in the closed-loop group vs. 166 mg/deciliter in the control group at both time points). At 26 weeks, the mean difference in glycated hemoglobin level was −0.33 percentage points (95% CI, −0.53 to −0.13; P=0.001). 17 adverse events occurred in the closed-loop group compared to 2 in the control group, but nearly all were determined to have been caused by infusion set failures.
Image: PD
©2019 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.