Empagliflozin reduces the risk of long-term renal effects in type 2 diabetes
1. In patients with type 2 diabetes and an estimated glomerular filtration (eGFR) rate of ≥ 30 mL per minute per 1.73 m2 of body-surface area that received empagliflozin, there was reduced incidence of new or worsening nephropathy, less incidence of doubling of creatinine and less initiation of renal-replacement therapy.
2. Adverse event rates were similar in the empagliflozin group to that reported in the overall trial population.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: The EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial demonstrated that empagliflozin reduced the risk of major cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes at high risk of cardiovascular events. This subsequent pre-specified analysis aims to determine the long-term effects of empagliflozin on the kidney.
In the empagliflozin group there was significantly less incident or worsening nephropathy, less incidence of doubling of creatinine and less initiation of renal-replacement therapy, as compared to placebo. There was no statistical difference between-group difference in the rate of incident albuminuria. Adverse event rates in patients with impaired kidney function on empagliflozin were similar to that reported in the overall trial population. Strengths of this study include it being a large, multi-centre, placebo-controlled double-blinded trial. It also studied the important outcome of renal replacement therapy. However, this trial had low enrollment of black patients and thus impacts the generalizability to this important patient population.
Click to read the study, published today in NEJM
Relevant Reading: Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: The EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial was a multi-centre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. The study population included patients with type 2 diabetes, established cardiovascular disease and eGFR of at least 30mL/min/1.73 m2 of body-surface area determined by the MDRD eGFR equation. Patients were then randomly assigned to receive empagliflozin (10 mg or 25 mg daily) or once daily placebo. This separate analysis looked at microvascular outcomes. Specifically, incident or worsening nephropathy (defined as progression to macroalbuminuria), doubling of the serum creatinine and a decrease of eGFR to ≤ 45 mL/min/1.73 m2 of body-surface area, initiation of renal-replacement therapy or death from renal disease. Statistical analysis included a modified intention-to-treat approach with Cox proportional hazards to assess between group differences in risk.
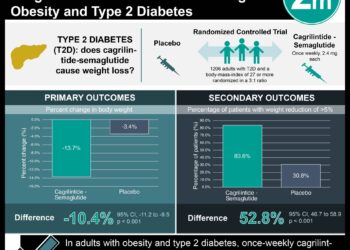
The proportion of individuals that had an incident or worsening nephropathy were 12.7% in the empagliflozin group and 18.8% in the placebo group (HR 0.61; 95%CI 0.53-0.70, p < 0.001). Doubling of creatinine level occurred in 1.5% of those on empagliflozin and 2.6% in the placebo group, relative risk reduction of 44%. There was also a significant decrease in initiation of renal replacement therapy, 0.3% in the empagliflozin group and 0.6% in the placebo group, a 55% relative risk reduction. There was no significant difference in incident albuminuria. Adverse events in patients with baseline impaired kidney function and on empagliflozin were similar to those reported in the overall trial population.
Image: PD
©2016 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.