Guided patient self-management of blood pressure medications effective
1. Self-monitoring followed by self-titration of anti-hypertensive medications using an individualized algorithm significantly lowered blood pressure in patients at high-risk of adverse cardiovascular events.
2. There was no difference in the incidence of adverse effects from anti-hypertensive medications in the two groups.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Adequate blood pressure control is crucial to decreasing the risk of adverse cardiovascular outcomes. The Telemonitoring and Self-Management in Hypertension 2 (TASMINH 2) trial previously found that self-monitoring and self-titration of blood pressure medications led to a significantly lowered systolic blood pressure after 12 months compared to usual care. However, the trial included very few individuals with conditions such as diabetes or chronic kidney disease. Therefore this current study specifically examined the effects of self-management of blood pressure in patients at a higher risk of cardiovascular events. Patients were randomized to either usual care or self-monitoring of blood pressure and self-titration of anti-hypertensive medications using an individualized algorithm. The primary outcome was difference in systolic blood pressure after 12 months.
This study demonstrated that patients high-risk for adverse cardiovascular events were able to achieve statistically and clinically significant decreases in blood pressure by self-monitoring and self-titrating anti-hypertensive medications using an algorithm developed with their family physicians. Patients experienced a gradual but sustained decrease in blood pressure. Strengths included the recruitment of patients from an array of family practices in the UK. However, patients were largely white and well-educated, bringing into question the generalizability of this study. Overall, this study suggests that individuals at high-risk of cardiovascular disease with uncontrolled hypertension may benefit from self-management of blood pressure.
Click to read the study, published today in JAMA
Click to read the accompanying editorial, published today in JAMA
Relevant Reading: 2014 Evidence-Based Guideline for the Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults(JNC 8)
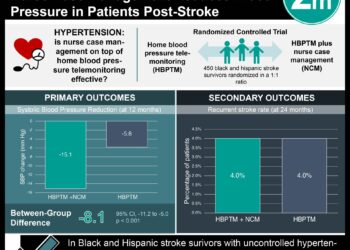
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: Of the 450 people included in the primary analysis, 220 were randomized to intervention and 230 to usual care. In the control group, the mean baseline blood pressure was 143.6/79.5 mmHg while in the intervention group, it was 143.1/80.5 mmHg. After 12 months, the intervention group mean blood pressure was 137.8/76.3 mmHg while the control group mean blood pressure was 128.2/73.8 mmHg. This represents a difference of 9.2 mmHg (95% CI, 5.7-12.7) and 3.4 mmHg (95% CI, 1.8-5.0) in systolic and diastolic blood pressures, respectively. Although prescription of anti-hypertensive drugs increased in both groups over the 12 months in the study, a greater increase was noted in the intervention group. However, there were no significant differences between the two groups with regards to the percentage of patients who experienced adverse effects of anti-hypertensive medications were noted (p>0.10 in the ten most frequently reported adverse effects).
More from this author: Stroke within past 9 months linked with adverse surgical outcomes, Home initiation of HIV care increases anti-retroviral therapy use in Malawi, Immune-modulating enteral nutrition does not reduce infections in the ICU,Flexible sigmoidoscopy decreases colorectal cancer incidence and mortality
Image: PD
©2012-2014 2minutemedicine.com. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2minutemedicine.com. Disclaimer: We present factual information directly from peer reviewed medical journals. No post should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors, editors, staff or by 2minutemedicine.com. PLEASE SEE A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IN YOUR AREA IF YOU SEEK MEDICAL