HbA1c may increase with switch from analogue to human insulin
1. In this retrospective cohort study, mean HbA1c levels decreased prior to systematic implementation of a program to switch from analogue to human insulin, after which HbA1c levels then increased slightly and remained steady.
2. Serious hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic events were not significantly different with program implementation.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Study Rundown: The price of insulin has substantially increased in recent years, which has translated into higher out-of-pocket expenses for patients with insufficient drug coverage. Newer analogue insulin medications are more expensive than human insulin products, but the benefit in clinical outcomes is unclear. In this retrospective cohort study, HbA1c levels were assessed in diabetes patients before and after systemic implementation of a program to switch from analogue to human insulin. HbA1c decreased in the population prior to program implementation but increased minimally with program implementation. No significant changes in HbA1c levels were detected during the post-intervention period compared to the intervention period Further, serious hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic events were not significantly different with program implementation.
Overall, this study suggested that switching from analogue to human insulin may lead to slightly higher HbA1c levels. The study is limited by its retrospective design and the possibility of residual confounding or time-related biases. Further research would be helpful to understand the economic impact and clinical relevance of small increases in HbA1c over a longer period with this switch.
Click to read the study, published today in JAMA
Click to read an accompanying editorial in JAMA
Relevant Reading: Strategies to improve the affordability of insulin in the USA
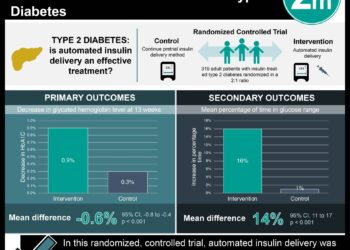
In-Depth [retrospective cohort]: This closed cohort study (n = 14635) out of Brigham and Women’s Hospital utilized data from a managed care organization that is a Medicare Advantage plan and subsidiary group based in California, serving members in 4 states including California, Arizona, Nevada, and Virginia. The program began to switch patients from higher-cost analogue to lower-cost human insulin regimens in 2015 and tracked patients until 2016. The primary outcome was overall glycemic control measured by mean monthly HbA1c, and secondary outcomes were serious hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic events. HbA1c levels were estimated over three 12-month periods: pre-intervention (baseline) in 2014, intervention in 2015, and post-intervention in 2016. Mean HbA1c was 8.46% at baseline and decreased at a rate of -0.02% per month prior to intervention (p < 0.001). There was a 0.14% increase in HbA1c associated with the start of intervention (p < 0.001). No statistically significant differences in mean HbA1c levels were found (p = 0.09) during the post-intervention period compared to the intervention period. Further, serious hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic events were not significantly different with program implementation (p > 0.05).
Image: PD
©2019 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.