Levodopa for Parkinson’s disease more effective than newer generation therapies
1. Levodopa provided a small but consistent benefit for treatment of Parkinson’s disease as compared to levodopa-sparing regimens including dopamine agonists and monoamine oxidase B inhibitors (MAOBIs).
2. Among levodopa sparing regimens, MAOBIs were at least as effective as dopamine agonists.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Study Rundown: The optimal treatment in the initial stages of Parkinson’s disease is currently uncertain. While levodopa appears to control motor symptoms better than either monoamine oxidase B inhibitors (MAOBIs) or dopamine agonists, it also carries the highest risk for dyskinesias. MAOBIs and dopamine agonists; however, have a greater risk of causing non-motor side effects such as nausea and sleep disturbance. The authors of this study undertook the largest trial to date in order to identify the optimal treatment for Parkinson’s disease. The study found that there was a very small but persistent benefit in patient-rated mobility scores when treatment had been initiated with levodopa. The investigators also observed that MAOBIs was at least as effective as dopamine agonists. This study was strengthened by the large sample size. The focus on quality of life measures rather than control of motor symptoms provided a more holistic view of patient experience that has not been performed in prior research. This study, however, was limited by the fact that neither the patients nor investigators were blinded to the treatment conditions, introducing potential bias in the reports made by patients and observations made by investigators.
Click to read the study, published today in The Lancet
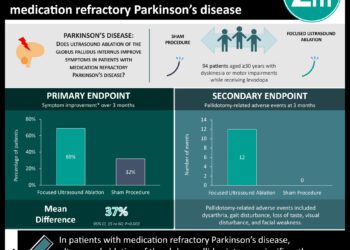
In-Depth [randomized, open-label trial]: This study included 1620 patients diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease who were randomly assigned to receive levodopa, MAOBI, or dopamine agonists. Outcomes for the study included patient rated functional status according to the 39-item Parkinson’s Disease Questionnaire (PDQ-39), quality-adjusted life-years calculated from the EuroQol EQ-5D, as well as cognition, dyskinesia, hospital or institutional admissions, and mortality.
The authors found that PDQ-39 mobility scores were 1.8 (95% confidence interval, CI, 0.5 – 3.0, p = 0.005) points higher in patients who received levodopa than those who received levodopa-sparing treatment. EQ-5D utility scores were also better in patients receiving levodopa with scores being 0.03 (95% CI 0.01 – 0.05; p = 0.0002) points higher than those receiving levodopa sparing treatment. Rates of dementia, institutional admission, and mortality were not significantly different between the two groups. Patients in the levodopa group were more likely to develop dyskinesias compared to the levodopa-sparing group (hazard ratio [HR] 1.52, 95% CI 1.16-2.00, p = 0.003).
More from this author: Schizophrenia linked with higher rates of violence, suicide, and early mortality;Overall improvement in management of high blood pressure between 1994 and 2011;Link between early life antibiotic use, asthma exacerbations, and impaired viral immunity;Structural and neurobiological foundations of suicide, a review;Buccal administration of dextrose gel effective in treatment of neonatal hypoglycemia
Image: PD
©2012-2014 2minutemedicine.com. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2minutemedicine.com. Disclaimer: We present factual information directly from peer reviewed medical journals. No post should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors, editors, staff or by 2minutemedicine.com. PLEASE SEE A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IN YOUR AREA IF YOU SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE OF ANY SORT.