Rapid antigen-based home testing reduced SARS-CoV-2 transmission and mortality
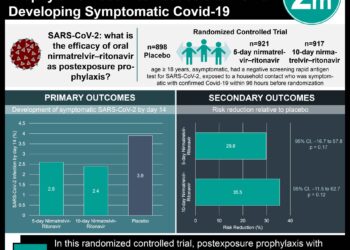
1. Base-case analysis for weekly testing availability predicted large reductions in infections, hospitalizations, and mortality.
2. The cost per death averted varied dramatically according to behavioral responses but remained well below the range of commonly accepted values of a statistical life.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Study Rundown: A number of strategies have been verified and adopted as cornerstones for containing the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. High-frequency, home-based antigen testing, however, has generated significant controversy. While the speed and accessibility of this tool are advantages, critics cite the relatively low specificity and sensitivity of this type of testing as major drawbacks. This study utilized a simple compartmental epidemic model of the United States over 60 days to quantify these contentions. The study determined the testing intervention would be effective and cost-effective in preventing infections, hospitalizations, and deaths. The model was also robust, predicting the cost per death averted would remain below the minimum benchmark value of a statistical life. The study was limited by the model-based evaluation and the benefits posed in densely populated locations such as schools and concerts. Nonetheless, these findings are significant, as they suggest the implementation of a mass testing program would likely be highly worthwhile in the general population.
Click here to read the study in Annals of Internal Medicine
Relevant Reading: Evaluation of a SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen test: Potential to help reduce community spread?
In-Depth [prospective cohort]: This study involved a 60-day projection of the United States population with variable parameters corresponding to hypothetical test performance (and behavioral responses. Input data were informed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guidance and existing literature. The study assessed health outcomes and economic performance. In the base case analysis, weekly home testing reduced infections from 11.6 million to 8.8 million and deaths from 119,000 to 103,000. Inpatient costs were slightly reduced from $6.5 billion to $5.9 billion, but losses in productivity increased from $3.5 billion (19.6 million days) to $14 billion (78 million days). Test kits were projected to cost an additional $12.5 billion. Despite this overall monetary increase, the cost per infection averted was $7890, and the cost per death averted was $1.43 million, a value well below the most stringent recommended benchmark of $5.3 million per statistical life (central estimate, $11.3 million; upper bound, $17.2 million). In the worst-case behavioral scenario (25% participation; 25% isolation of persons with positive results; 33% rate of daily abandonment), the cost per death averted increased to $4.1 million, but the number of infections was still reduced by over 600,000. Overall, the use of weekly testing reduced infections, hospitalizations, and mortality.
Image: PD
©2021 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.