Self-monitoring of glucose in non-insulin dependent diabetics not linked to improved control
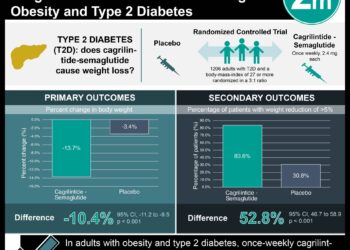
1. In this randomized, open-label trial, glucose self-monitoring in patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus with or without electronic feedback was not associated with improved glycemic control or health related quality of life (HRQOL) at one year compared to usual care.
2. While there was short-term improvement in glycemic control in the intervention arms, it did not last at one year, and there was a significant decrease in compliance in blood glucose monitoring arms.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Type 2 diabetes mellitus remains a common and increasingly prevalent condition associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Improved glycemic control has been linked to improved clinical outcomes and is best achieved through a combination of lifestyle changes, dietary modification, and pharmacologic control. Though commonly recommended, self-monitoring of glucose in non-insulin dependent diabetics has not been conclusively shown to improve glycemic control and yet may be associated with increased health care cost and discomfort for patients. This was a randomized, open-label trial that examined the effectiveness of patient daily self-monitoring of glucose with or without electronic feedback on results compared to no monitoring. While initially both intervention groups demonstrated improved HbA1c values, there was reduced compliance by one year and no significant differences compared to control.
The primary care setting in which the trial was conducted reflected the real work setting and the randomized design improved the overall strength of the study. The main limitations included the patient exposure to endocrinologist in certain situations, and inclusion of patients with extremes of HbA1c values, both of which added extraneous variable to the study.
Click to read the study, published in JAMA Internal Medicine
Relevant Reading: Evidence of a Strong Association Between Frequency of Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose and Hemoglobin A1c Levels in T1D Exchange Clinic Registry Participants
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: This study included patients from 15 primary care sites with a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes who were 30 years or older and had HbA1c levels at baseline between 6.5% and 9.5%. Patients were excluded if they were to be seen by an endocrinologist within one year, planned to use insulin in the study period, or were planning on moving or becoming pregnant. The main intervention included once daily glucose monitoring with an addition group having enhanced feedback with automated, encouraging messaging along with the glucose measurement. The primary outcomes included change in HbA1c levels at one year, and HRQOL as assessed by the physical and mental components of the Short Form 36 questionnaire.
A total of 450 patients were included in the study, with patients balanced with respect to age, gender, race, BMI, comorbidities, and use of hypoglycemic agents. At one year follow up there was no difference in HbA1c or HRQOL scores between the control or intervention groups. HbA1c values were lower at 6 months (p = 0.001) for both intervention groups, but were the same as control by one year. The compliance with daily glucose monitoring had fallen throughout the study in both intervention arms, dropping to 50-60% by 1 year.
Image: PD
©2017 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.