#VisualAbstract: 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure better predicts all-cause mortality than clinic blood pressure
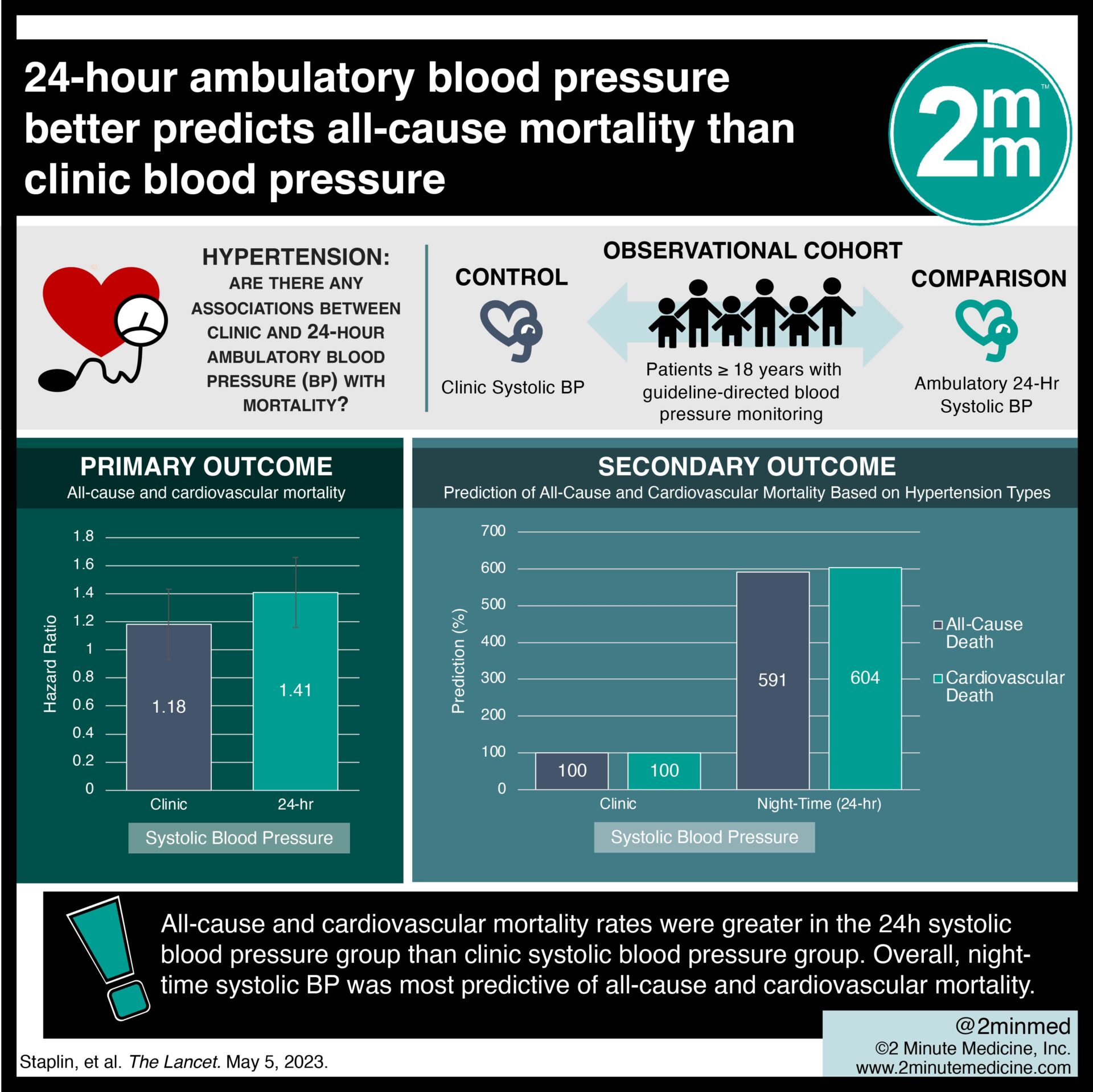
1. All-cause and cardiovascular mortality rates were greater in the 24h systolic blood pressure group than clinic systolic blood pressure group.
2. Night-time systolic blood pressure was most predictive of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Study Rundown: Hypertension is often known as one of the leading causes of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. While studies suggest that ambulatory monitoring better predicts actual blood pressure compared to measurements taken in the clinic, this association remains unclear. This observational cohort study aimed to determine the association of clinic and 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure with mortality among patients with hypertension. The primary outcome of this study was all-cause and cardiovascular mortality while key secondary outcomes included hypertension types. According to study results, ambulatory blood pressure was more predictive of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with known hypertension compared to clinic blood pressure. This study was strengthened by a longitudinal median follow-up with patients from various centers across Spain, thus increasing the validity of findings.
Click to read the study in The Lancet
Relevant Reading: Trial of Intensive Blood-Pressure Control in Older Patients with Hypertension
In-depth [retrospective cohort]: Between Mar 1, 2004, and Dec 31, 2014, 59 124 patients were included from 223 primary care centers in 17 regions of Spain. Included were patients ≥ 18 years with guideline-directed blood pressure monitoring. The primary outcome of all-cause mortality was greater in the 24h systolic blood pressure group (hazard ratio [HR] 1.41, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.36-1.47) than in the clinic systolic blood pressure group (HR 1.18, 95% CI 1.13-1.23). Moreover, night-time systolic blood pressure was most predictive of all-cause mortality (591%) and cardiovascular mortality (604%) with the latter being significantly elevated in patients with masked hypertension (HR 1.24, 95% CI 1.12-1.37) and sustained hypertension (HR 1.24, 95% CI 1.15-1.32). Findings from this study suggest that nighttime ambulatory blood pressure monitoring better predicts all-cause mortality than clinic blood pressure.
Click here to read this study in NEJM.
©2023 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. 1.