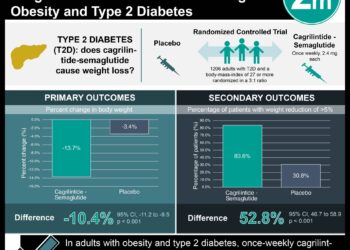
#VisualAbstract: Combined cagrilintide and semaglutide for weight management well-tolerated in early clinical trials
1. Semaglutide 2.4 mg combined with once weekly cagrilintide therapy was not associated with increase in adverse events compared to semaglutide alone.
2. Compared to control, combined cagrilintide and semaglutide improved glycemic parameters and mean body weight reduction at 20 weeks.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Semaglutide is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogue currently approved to treat type 2 diabetes and is being studied for weight management in diabetes. Cagrilintide is a long-acting amylin analogue that antagonizes endogenous amylin and calcitonin receptors, a drug currently being investigated for weight loss. This randomized, placebo-controlled, multiple-ascending dose, phase 1b trial aims to evaluate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics increasing cagrilintide doses (0.16 – 4.5 mg) vs. placebo, both given in combination with semaglutide 2.4 mg. Participants were randomly assigned to six cohorts, maintained baseline level of activity, and were followed for 20 weeks during this trial. The results of this study demonstrate that overall, combined cagrilintide and semaglutide therapy is well-tolerated and the safety profile is comparable to semaglutide alone. In particular, gastrointestinal disturbance, an expected side effect of these medications, was comparable among combined therapy and placebo groups. Early satiety and decreased appetite were reported as adverse events associated with higher doses of cagrilintide. Pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic parameters were dose-dependent. Overall, this phase 1b trial demonstrates that combined cagrilintide and semaglutide therapy is safe, well-tolerated, and offers clinically meaningful weight loss compared to placebo, warranting further investigation for weight management in obesity.
Click to read the study in The Lancet
Relevant Reading: Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: This study recruited individuals aged 18-55 years with a body-mass index 27.0−39.9 kg/m2 from a single center. Participants (n=96) were randomly assigned to once weekly subcutaneous cagrilintide (0.16, 0.30, 0.60, 1.2, 2.4, or 4.5 mg) or injection volume-matched placebo in a 3:1 ratio. Demographics and participant characteristics were comparable between groups. All intervention and placebo groups received subcutaneous semaglutide 2.4 mg injections once weekly. The cagrilintide and semaglutide doses were escalated every 4 weeks, with final dose achieved at 16 weeks. No lifestyle modifications were initiated. Primary endpoint was defined as adverse events associated with treatment. Secondary endpoints were defined as pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetic parameters including maximum serum concentration, time to maximum concentration, half-life, plasma clearance, and volume of distribution, as well as exploratory parameters including bodyweight, glycemic control, and overall hormone profile. Adverse events were mild to moderate in severity, most commonly gastrointestinal disturbance (207 adverse events, 37%), with similar rates across treatment groups. Maximum plasma concentration of cagrilintide was reached at 19 weeks, with half-life ranging between 159–195 hours. The half-life of semaglutide ranged between 145–165 hours and was not affected by cagrilintide dosing. In patients receiving cagrilintide 2.4 mg plus semaglutide, there was a mean body weight change from baseline of -17.1% compared to -9.8% with semaglutide alone. This study is limited by the relatively short 20-week follow-up time. Additionally, this study was designed to investigate safety and tolerability, thus secondary weight management outcomes must be interpreted in context. Despite these limitations, this study validates the safety of combined cagrilintide and semaglutide pharmacotherapy, justifying additional studies to evaluate efficacy for weight management in obesity.
Image: PD
©2021 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.