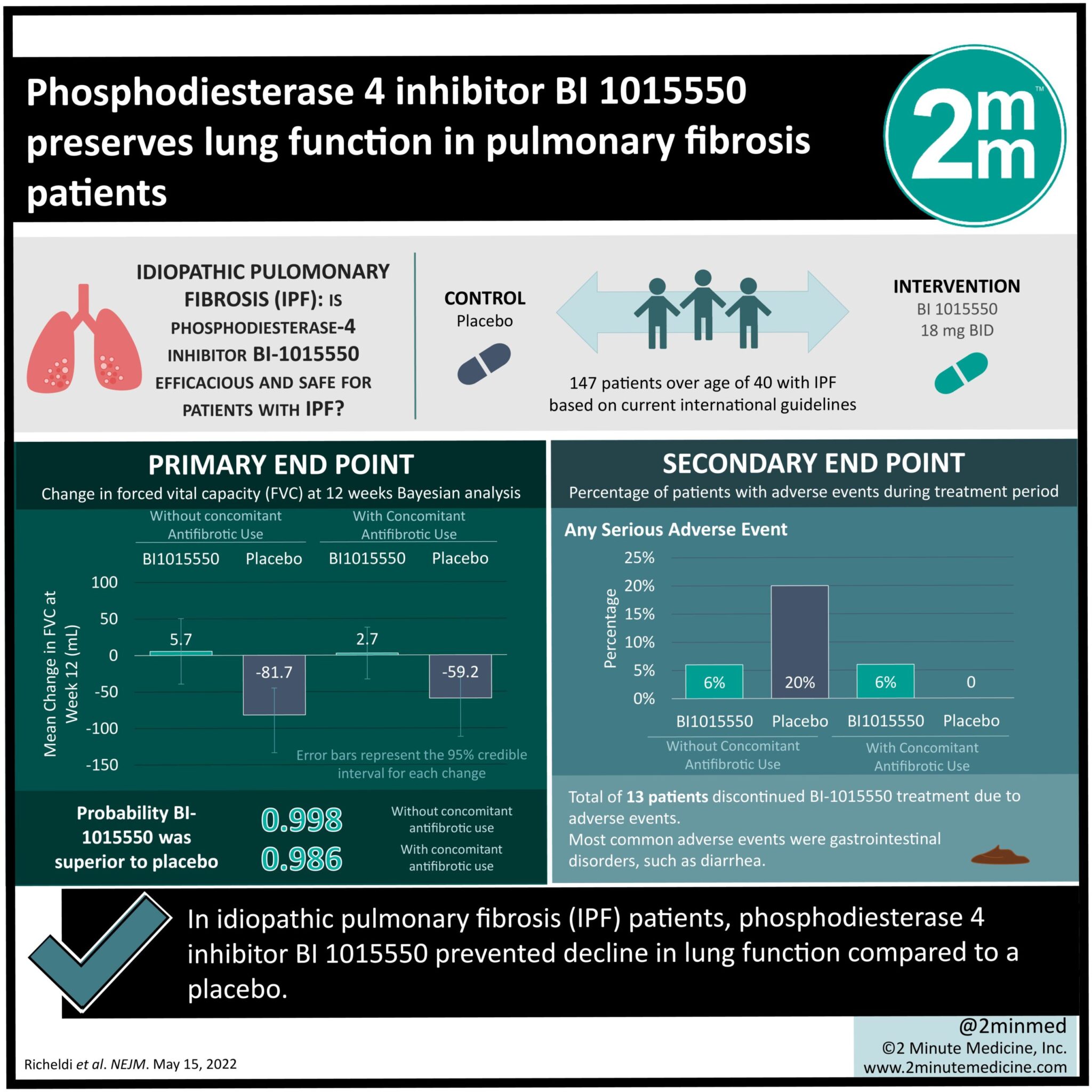
#VisualAbstract: Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor BI 1015550 preserves lung function in pulmonary fibrosis patients
1. In idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) patients, phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor BI 1015550 prevented decline in lung function compared to a placebo.
2. Incidence of adverse events, consisting mostly of gastrointestinal disorders, was higher in the BI 1015550 group compared to the placebo group.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Currently approved antifibrotic medications, such as nintedanib and pirfenidone, are unable to completely prevent the progression of fibrosis in patients with IPF. Progression of fibrosis in this population can have a devastating impact on prognosis as well as quality of life. This phase two randomized control trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of BI 1015550 as compared to placebo control. BI 1015550 is an oral preferential inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 4 enzyme, a key driver of IPF progression. Each group received two daily doses of the drug or placebo for 12 weeks. Patients were followed for one week after completion of the regimen. Regardless of the presence or absence of concomitant antifibrotic agents, lung function, as measured by forced vital capacity, decreased in the placebo group, while remaining stable in the BI 1015550 group. The study group reported a higher percentage of patients with adverse events, several of which led to the discontinuation of BI 1015550. The most common adverse events were diarrhea and fatigue. The limitations of this study include the small sample size and short treatment regimen and follow-up duration, which limited the generalizability of the results.
Click to read the study in NEJM
Relevant Reading: Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: In the present study, IPF patients over the age of 40 with (n=74) and without (n=73) background antifibrotic use were randomly assigned to receive BI 1015550 or placebo treatment in a 2:1 ratio. Patients received two daily doses of the drug or placebo for 12 weeks and were followed up for one week after completion. The study used the Bayesian and mixed model with repeated measures (MMRM) approaches to conduct analysis. Both the Bayesian and MMRM approaches demonstrated a more significant decline in forced vital capacity (FVC) in the placebo group compared to BI 1015550 group. In the more conservative Bayesian analysis, the median change in FVC from baseline to week 12 in the BI 1015550 and placebo groups was 5.7mL (credible interval, -39.1 to 50.1) and -81.7mL (95% credible interval, -133.5 to -44.8) respectively among patients without concomitant antifibrotic use, and 2.7mL (95% credible interval, -32.8 to 38.2) and -59.2mL (95% credible interval, -111.8 to -17.9) respectively among patients with concomitant antifibrotic use. There was a higher incidence of adverse events in the BI 1015550 group compared to the placebo for both patients with (65% and 52% for BI 1015550 and placebo groups respectively) and without (73% and 68% for BI 1015550 and placebo groups respectively) concomitant antifibrotic use. Adverse events for 13 patients led to the discontinuation of BI 1015550. No patients discontinued the placebo. Diarrhea was the most common adverse event. Future phase three trials in larger study cohorts are necessary to support the therapeutic effects and safety of BI 1015550 for IPF.
©2022 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.


![2MM: AI Roundup- AI Cancer Test, Smarter Hospitals, Faster Drug Discovery, and Mental Health Tech [May 2nd, 2025]](https://www.2minutemedicine.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/Untitled-design-350x250.png)


![The ABCD2 score: Risk of stroke after Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) [Classics Series]](https://www.2minutemedicine.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/05/web-cover-classics-with-logo-medicine-BW-small-jpg-75x75.jpg)