Adolescent misuse of prescription opioids may lead to heroin use in adulthood
1. This quantitative study of high school seniors between 1976-2000 found that nearly 1 in 3 high school seniors who misused prescription opioids as high school seniors later used heroin by age 35.
2. The study also found that increased opioid prescriptions in the 1990s and 2000s may have led to increased opioid overdoses in recent years.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Opioid misuse and overdoses are a major problem in the United States. One factor that may be leading to the rate of heroin dependence is the growing population of youth with a history of nonmedical use of prescription opioids. However, there is a paucity in research examining the association between the prospective use of medical and nonmedical opioid misuse during adolescence, and future heroin use in adulthood.
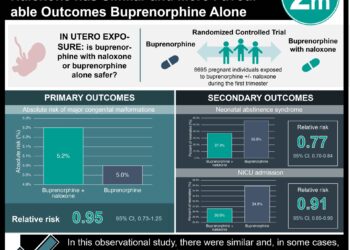
This quantitative study analyzed self-reported responses about drug use from 11,012 adolescents over 17 years in the national Monitoring the Future study. Adolescents in 12th grade from 25 cohorts spanning 1976-2000 who provided at least 1 wave of follow-up data (at the age of 30 and/or 35) were included. Participants were divided into five different categories based on opioid usage at the age of 18: 1) no lifetime exposure (control group); 2) medical prescription use; 3) medical use followed by nonmedical misuse; 4) nonmedical misuse followed by medical use; 5) nonmedical misuse only. Participants who reported lifetime heroin use at 18 were excluded. Primary outcome assessed for any heroin use through age 35.
When subgroups were compared amongst one another for heroin use through age 35, the researchers found that those who reported nonmedical prescription opioid use had the highest odds of heroin use by age 35. Adolescents who reported medical opioid use also were at greater risk. One limitation of this study may be the fact that the data was self-reported. Nonetheless, this study’s findings may hold value in determining which patients may be high-risk for developing heroin addiction later in life. Furthermore, these findings indicate the importance of vigilant monitoring after opioid prescriptions early in life.
Click to read the study in Journal of Addiction Medicine
Image: PD
©2021 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.