Antibody testing may provide diagnostic support for SARS-CoV-2 infection
1. Antibody testing to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection was shown to provide diagnostic support for patients who tested negative by nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) but remained clinically suspicious for the infection.
2. Antibody testing to SARS-CoV-2 was shown to contribute to the existing infection serology diagnosis.
Evidence Rating Level: 3 (Average)
Study Rundown: The gold standard for COVID-19 diagnosis is nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT), although there are limitations to the test arising from intermittent viral shedding and nasopharyngeal swab techniques. Serologic testing for COVID-19 is used throughout public health for patient diagnostics and can serve as a complementary test to NAAT. However, the clinical applications of serologic testing for COVID-19 are undefined. As such, this study determined the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein serum assay’s ability to present antibody kinetics and subsequent clinical use. Results from antibody testing were able to provide diagnostic patient support when patients had tested negative through NAAT but remained at clinical suspicion for COVID-19. This case-control study was limited by its sampling of hospitalized patients. The convenience sampling in the study created a bias since patients who were asymptomatic carriers were not included in the antibody testing. Therefore, the findings of this study may not be generalized to the public. Nonetheless, this study was strengthened by showing the complementary benefit of antibody testing with NAAT for SARS-CoV-2.
Click to read the study in Annals of Internal Medicine
Relevant Reading: Treatment of 5 Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19 With Convalescent Plasma
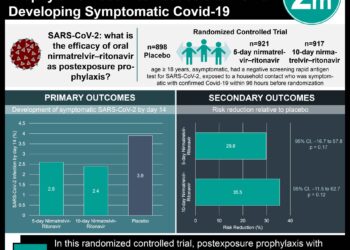
In-Depth [case-control study]: This case-control study included 628 participants from a single medical center. Participants were included if they had nasopharyngeal swab testing conducted between March 11, 2020, and April 12, 2020, testing conducted at Johns Hopkins University Medical Center, and NAAT testing conducted from nasopharyngeal swab samples. Participants with an absence of NAAT testing of nasopharyngeal swab samples were excluded. Based on these criteria, the cohort consisted of 11,066 tests within which, two groups were formed. The case group consisted of 115 hospitalized patients and the control group consisted of 513 participants. All of these participants underwent serum antibody testing for the presence of IgG and IgA antibodies against the S1 domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. The serum IgG antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 were significantly higher in the case group (median, 2.01 units, interquartile range [IQR], 0.16 to 44.33 units) compared to the control group (median, 0.10 units, IQR, 0.05 to 0.19 units; P < 0.001). Furthermore, serum IgG measurement at least 14 days after symptom onset distinguished case patients from the control group with a sensitivity of 0.976 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.928 to 0.995) and specificity of 0.988 (95% CI, 0.974 to 0.995). Serum IgA measurement within the same time frame had a similar sensitivity (0.984, 95% CI, 0.939 to 0.999) and lower specificity (0.880, 95% CI, 0.851 to 0.905). Finally, in patients who tested negative with NAAT but had high clinical suspicion of COVID-19 infection, serum antibodies for SARS were present in a subset of the case patients tested (5 out of 6, 83%), while antibodies were not present in the control group (0 out of 12, 0%). Taken together, the antibody testing for SARS-CoV-2 may provide diagnostic support for patients who have negative NAAT results but still have a high clinical suspicion of the infection.
Image: PD
©2020 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.