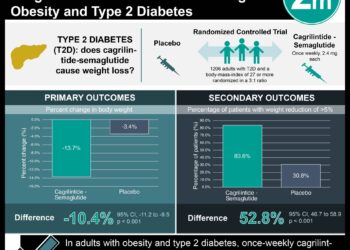
Bariatric surgery beneficial in type-2 diabetes, similar in cost to conventional treatment
1. Total health-care costs were higher for patients treated for obesity with bariatric surgery vs. conventional treatment if the patients were euglycemic or prediabetic prior to intervention.
2. However, total health-care costs were not significantly different for patients treated for obesity with bariatric surgery vs. conventional treatment if the patients were diabetic prior to intervention.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Severely obese patients have difficulty losing weight through lifestyle changes, however, bariatric surgery has been shown to sustain weight loss and improve or eliminate type-2 diabetes in most patients. This study assessed health-care costs in patients with obesity that underwent bariatric surgery or were treated conventionally. 4,030 patients in Sweden were allotted to subgroups according to pre-intervention glycemic status (eugylcemic, prediabetes, or type-2 diabetes) and followed for a period of 15 years. Data for each patient on prescription drug costs, inpatient, and outpatient visits was retrieved from national registers and compared by intervention type (surgical vs. conventional) and pre-intervention glycemic status.
Drug costs were not significantly different in the surgery and conventional treatment groups for the euglycemic subgroup, but were lower in the surgery group for the prediabetes and the diabetes subgroups. Inpatient costs were higher for all patient subgroups treated with surgery compared to conventional treatment for obesity. No significant differences in outpatient costs were observed for any subgroup. Total health-care costs were higher for patients treated with surgery in the euglycemic and prediabetes subgroups, but was shown to have no significant difference for patients with diabetes. These cost findings support the prioritization of treatment of obesity with bariatric surgery for patients with diabetes. Though this study was limited by non-randomization, it was the first to assess obesity treatment costs according to pre-intervention glucose status.
Click to read the study in The Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology
Relevant Reading Bariatric Surgery and Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes in Swedish Obese Subjects
In-Depth [prospective cohort]: This study assessed health-care costs for patients treated for obesity (BMI ≥ 34 in men and ≥ 38 in women) with either conventional treatment (lifestyle intervention, behavior modification, or no intervention) or bariatric surgery. In Sweden, 4,030 patients (aged 37-60 years) were followed for 15 years in subgroups according to pre-intervention glycemic status (2,836 eugylcemic, 591 prediabetes, and 603 type-2 diabetes). Cost data for prescription drugs and for inpatient and outpatient visits for each patient was retrieved from questionnaires, the Swedish Prescribed Drug Register, and the Swedish National Patient Register.
Drug costs were not significantly different in the surgery and conventional treatment groups for the euglycemic subgroup (surgery US$10,511 vs. conventional treatment $10,680; adjusted mean difference -$225 [95% CI -2,080 to 1,631]; p=0.812), but were lower in the surgery group for prediabetes ($10,194 vs. $13,186; -$3,329 [-5,722 to -937]; p=0.007), and diabetes ($14,346 vs. $19,511; -$5,487 [–7,925 to –3,049]; p<0.0001) subgroups. Inpatient costs were higher for all patient subgroups treated with surgery compared to conventional treatment for obesity (euglycaemic ($51,225 vs. $25,313; $22,931 [19,001–26,861]; p<0.0001), prediabetes ($58,699 vs. $32,861; $27,152 [18,736–35,568]; p<0.0001), and diabetes ($61,569 vs. $47,569; 18,697 [9,992–27, 402]; p<0.0001). No significant differences in outpatient costs were observed for any subgroup. Total health-care costs were higher for patients treated with surgery in the euglycemic ($71, 059 vs. $45,542; $22,390 [17,358–27,423]; p<0.0001) and prediabetes ($78,151 vs. $54,864; $26,292 [16,738–35,845]; p<0.0001) subgroups, but was shown to have no significant difference for patients with diabetes ($88,572 vs. $79,967; $9,081 [–1,419 to 19,581]; p=0.090).
Image: PD
©2015 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.