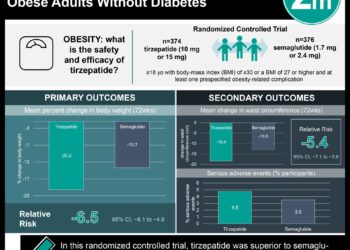
“Benign obesity” perhaps not so benign
Image: PD
1. Metabolically healthy obese individuals are at increased risk for death and CV events over the long term compared with their normal-weight counterparts.
2. All metabolically unhealthy individuals, regardless of BMI, had increased risk for events compared with metabolically healthy normal-weight individuals.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Study Rundown: Obesity (BMI ≥30 kg/m2) has been clearly linked to increased mortality; however, the association between overweight (BMI, 25 to 30 kg/m2) and mortality is less clear. One recent study found that mortality risk was actually lower among overweight individuals when compared to their normal weight counterparts. This and similar evidence have led some to propose that so-called “benign obesity” – having increased adiposity without abnormal metabolic features – may actually constitute an important subset of the overweight population. This meta-analysis aimed to elucidate the effect of metabolic status on risk for all-cause mortality and cardiovascular (CV) events in normal-weight, overweight, and obese persons and ultimately, to determine whether obesity in and of itself (ie absent metabolic derangement) is deleterious.
The findings of this analysis suggest that obese individuals have an increased risk for death and CV events over the long-term regardless of metabolic status. Moreover, being metabolically unhealthy regardless of BMI is associated with these adverse outcomes. The study did not, however, show a significant increase in mortality when comparing metabolically healthy overweight vs normal weight individuals, even when comparing these groups over a 10-plus year period. Further research is necessary to fully evaluate the concept of “benign obesity.” Future studies should incorporate lessons learned from this meta-analysis – namely, the importance of long-term follow-up and of categorizing participants not just by BMI but by metabolic status – to accurately characterize the risks associated with being overweight and obesity.
Click to read the study in Ann Int Med
Click to read an accompanying editorial in Ann Int Med
Relevant Reading: Body-mass index and cause-specific mortality in 900 000 adults: collaborative analyses of 57 prospective studies
In-Depth [systemic review and meta-analysis of observational studies]: This review aimed to evaluate the effect of metabolic status on risk for all-cause mortality and cardiovascular events in normal-weight, overweight, and obese persons. Reviewers identified studies published between 1950 and 2013 that evaluated all-cause mortality or cardiovascular events (or both) and clinical characteristics of patient groups defined by BMI category and metabolic status. In eligible studies, patients were categorized as normal weight, overweight, or obese by BMI and metabolically healthy vs unhealthy based on the presence or absence of components of the metabolic syndrome. The number of fatal and nonfatal CV events were then compared among individuals who were metabolically healthy and overweight, metabolically healthy and obese, metabolically unhealthy and normal weight, metabolically unhealthy and overweight, and metabolically unhealthy and obese (5 exposure groups) with the number of events in metabolically healthy people of normal weight (control group). Relative risks were calculated.
Eight studies (n = 61 386; 3988 events) were included. In a pooled analysis, metabolically healthy overweight individuals had a similar risk for all-cause mortality or CV events compared with metabolically healthy normal-weight persons (RR, 1.10; CI, 0.90 to 1.24). Mortality risk among metabolically healthy obese individuals was also similar to the reference group (RR, 1.19; CI, 0.98 to 1.38); however restricting analysis to studies with at least 10 years of follow-up elucidated a statistically significant increased mortality and CV risk (RR, 1.24; CI, 1.02 to 1.55) among obese individuals. All groups with unhealthy metabolic status (regardless of normal weight, overweight, or obesity) had increased risk. In both metabolically healthy and unhealthy subgroups, blood pressure, waist circumference, and insulin resistance increased, and HDL cholesterol decreased, across the BMI categories.
By Elizabeth Kersten and Andrew Bishara
More from this author: Outreach increases colorectal cancer screening among underserved; Clinical impression not reliable in identifying drug-seeking behavior; Industry influences on expert panels contribute to over-diagnosis; Undervaccination becoming more common, associated with increased patient admission rates; Overuse of colonoscopy widespread in the US; Silent myocardial infarctions more common than previously assumed
© 2013 2minutemedicine.com. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2minutemedicine.com. Disclaimer: We present factual information directly from peer reviewed medical journals. No post should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors, editors, staff or by 2minutemedicine.com. PLEASE SEE A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IN YOUR AREA IF YOU SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE OF ANY SORT.