LI-RADS outlines standards for liver imaging studies assessing HCC [Classics Series]
This study summary is an excerpt from the book 2 Minute Medicine’s The Classics in Medicine: Summaries of the Landmark Trials
1. The American College of Radiology (ACR) created the Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System (LI-RADS) to standardize interpretation and reporting of liver imaging studies assessing risk for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
2. Utilization of LI-RADS categories can aid in patient management decisions by suggesting diagnostic and/or treatment options.
Original Date of Publication: March 2011
Study Rundown: Chronic liver disease (CLD) and cirrhosis are risk factors for HCC, the third leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. With these factors contributing towards development of the disease, HCC can affect a wide range of communities and counties. Early stage HCC is often asymptomatic and detection earlier is associated with better outcomes when medical treatment is offered, making screening of patients at high risk for HCC a key intervention. Screening evaluations can be completed using a variety of methods, with computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) being the most common. LI-RADS, originally published in 2011 and continually updated, provides a standardized algorithmic framework for assessing HCC risk via CT or MRI. In addition to reducing variability in radiologist reporting, the framework can help clinicians by providing recommendations for how to follow-up lesions with further imaging studies, biopsies, and/or treatment. Though this system provides a standardized mechanism for lesion categorization, few prospective studies have been performed assessing how patients are differentially managed when assigned differing risk categories.
Click to read the LI-RADS Consensus Statement
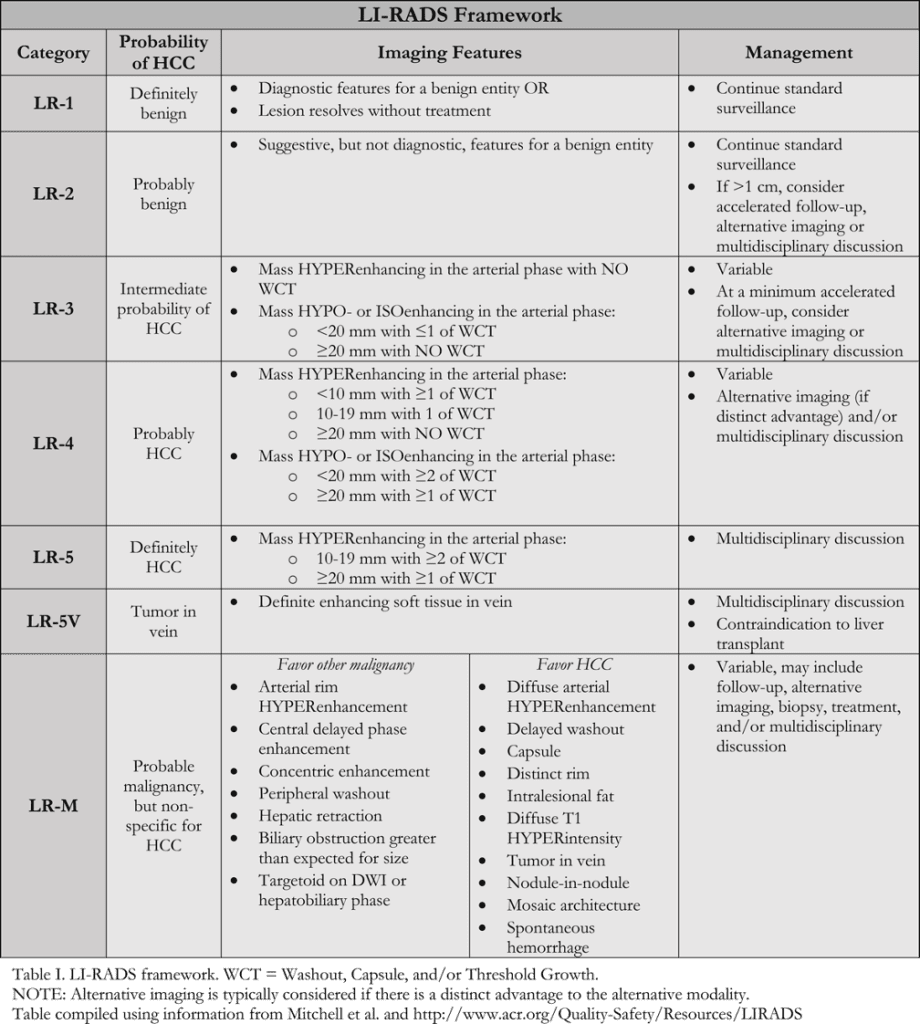
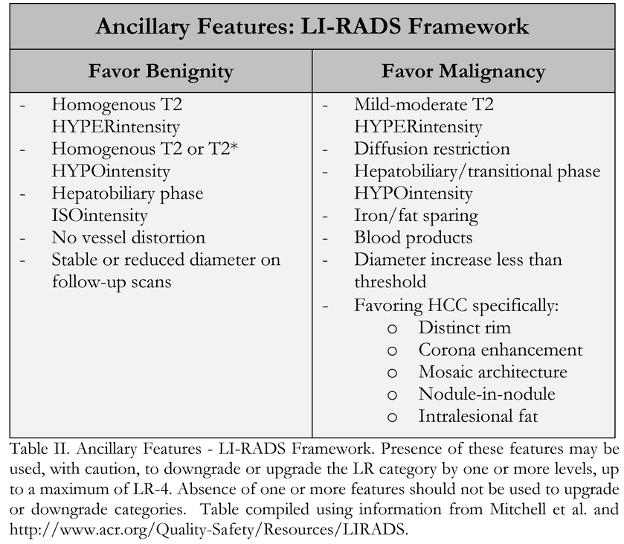
In-Depth [non-randomized trial]: LI-RADS was developed by a panel of radiologists, with additional contribution from hepatologists, liver surgeons, and pathologists. The first iteration was launched in 2011 and has been updated continually since. LI-RADS provides standardized terminology for interpreting hepatic lesions and categorizing them according to their risk of HCC based on image characteristics (Table I). Categorization ranges from “Definitely Benign” (LR-1) to “Definitely HCC” (LR-5). Categorization of lesions as “Probably Benign” (LR-2), “Intermediate Probability of HCC” (LR-3), and “Probably HCC” (LR-4) are based on 4 major image factors defined by Mitchell and colleagues including: arterial phase hyperenhancement; washout appearance following hyperenhancement; capsule appearance; and threshold growth compared with previous imaging. If there is uncertainty as to a categorization between LR-2 and LR-4, various defined ancillary image features may be used (Table 2). Additionally, there are categories for probable malignancy other than HCC (LR-M), previously treated HCC (LR5-T), and tumor within a vein (LR-5V).
Mitchell DG, Bruix J, Sherman M, Sirlin CB. LI-RADS (Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System): Summary, discussion, and consensus of the LI-RADS Management Working Group and future directions. Hepatology. 2015 Mar 1;61(3):1056–65.
Additional Review:
ACR. Archive – LI-RADS [Internet]. 2011. Available from: http://www.acr.org/Quality-Safety/Resources/LIRADS/Archive.
Purysko AS, Remer EM, Coppa CP, Leão Filho HM, Thupili CR, Veniero JC. LI-RADS: A Case-based Review of the New Categorization of Liver Findings in Patients with End-Stage Liver Disease. RadioGraphics. 2012 Nov 1;32(7):1977–95.
©2022 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.



![2MM: AI Roundup- AI Cancer Test, Smarter Hospitals, Faster Drug Discovery, and Mental Health Tech [May 2nd, 2025]](https://www.2minutemedicine.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/Untitled-design-350x250.png)


![The ABCD2 score: Risk of stroke after Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) [Classics Series]](https://www.2minutemedicine.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/05/web-cover-classics-with-logo-medicine-BW-small-jpg-75x75.jpg)
