The 2 Minute Medicine Podcast Episode 19
July 13th 2023
Welcome to the 2 Minute Medicine Podcast, summarizing the latest medical studies, curated and written by practicing physicians. On this podcast, twice a month, we cover the latest in healthcare news and research evidence.
Our episode is live!
Episode Description
We begin this episode by discussing our article of the week from the New England Journal of Medicine entitled “Ketamine versus ECT for Nonpsychotic Treatment-Resistant Major Depression.”In the second half of our episode, we begin with a discussion about how the Supreme Court of the United States may impact college admissions for the foreseeable future. Then we explore the latest information regarding the link between a beloved artificial sweetener, and cancer. Last, but not least, we have a conversation about blood clots along with the stars who have experienced them, and psychedelics, a class of drugs recently approved for mental health treatment in Australia!
Click here to listen to this episode on Apple podcast
Click here to listen to this episode on Spotify
 Transcript
Transcript
[Deepti] Welcome to the 2 Minute Medicine Podcast, summarizing the latest medical studies, curated and written by practicing physicians.
For our full suite of daily medical study summaries and updates written by practicing doctors, please visit our website at 2minutemedicine.com to start reading new daily content right now, for free. On this podcast, twice a month, we cover the latest in health care news and research evidence. We are your hosts Deepti and Andrew. On today’s episode, we’ll start off by discussing our two articles of the week. In the second half of the episode, we will look at health issues that have arisen in popular media.
[Andrew] Our article of the week comes from the New England Journal of Medicine and is entitled “Ketamine versus ECT for Nonpsychotic Treatment-Resistant Major Depression.”
Major depressive disorder is a leading cause of disability worldwide. Although pharmacologic antidepressants are standard of care, approximately one-third of patients have suboptimal responses. Treatment-resistant major depression (or TRMD) is defined as depression with an unsatisfactory response to at least two trials of antidepressants. ECT is a well-established modality for treating TRMD but remains underutilized due to limited access and concerns about its adverse effects. Ketamine, at subanesthetic doses, has emerged as a potential treatment for TRMD. Though, the relative efficacy and safety of ketamine compared to ECT has not been elucidated.
The current study was an open-label, randomized, noninferiority trial to evaluate ketamine compared to ECT for the treatment of TRMD without psychosis. Those between 21 and 75 years of age with TRMD without psychosis and a score greater than 20 on the Montgomery–Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (or MADRS) were included. Exclusion criteria included bipolar disorder, psychotic disorders, developmental disorders, and contraindications to ECT or ketamine.
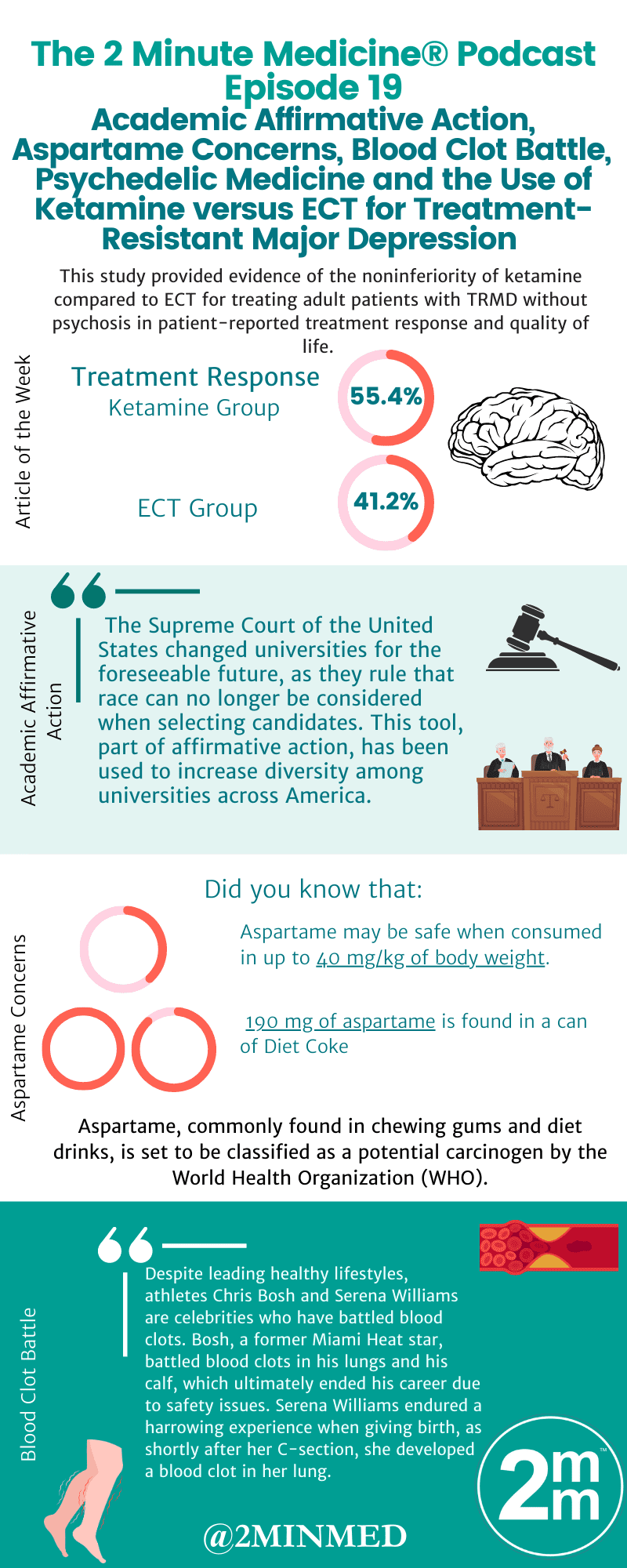
Overall, 403 patients were randomized 1:1 to receive ECT three times per week or intravenous ketamine infusion at 0.5 mg/kg twice per week. The primary outcome was a response to treatment, defined as a decrease of ≥50% from baseline in the score on the Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology – Self-Report [QIDS-SR-16]). By three weeks, 55.4% of patients treated with ketamine and 41.2% of those receiving ECT reported a response (difference, 14.2 percentage points; 95% Confidence Interval, 3.9 to 24.2; p<0.001). Both MADRS-defined treatment response and quality of life measures demonstrated the noninferiority of ketamine compared to ECT.
The ECT group reported a mean decrease in memory tests after three weeks. However, upon follow-up at one and six months, this score had normalized and was comparable between the two groups. Muscle pain and weakness were reported more frequently following ECT (5.3%) than ketamine infusion (0.5%) while ketamine was associated with higher scores of dissociative symptoms.
In summary, this study provided evidence of the noninferiority of ketamine compared to ECT for treating adult patients with TRMD without psychosis in patient-reported treatment response and quality of life. ECT was associated with decreased memory recall at three weeks, which recovered upon follow-up, and myalgias. Conversely, Ketamine was associated with dissociation. The trial was limited by its open-label design and the lack of a placebo or maintenance treatment.
[Andrew] Now for The Scan.
The Story: The Supreme Court of the United States changed universities for the foreseeable future, as they rule that race can no longer be considered when selecting candidates. This tool, part of affirmative action, has been used to increase diversity among universities across America.
You might be wondering, what is Affirmative Action?
[Deepti] Great question. To improve diversity and ensure equal opportunities for those disproportionately affected by historical events, affirmative action aims to eliminate discrimination and afford opportunities to marginalized populations. One such effort is the use of race in college admissions, to ensure a diverse population and inclusion of minority groups. After this ruling, it is the elite schools and programs who anticipate a considerable demographic change, due to patterns observed in states who have already eliminated affirmative action.
One highly selective program that is preparing for change, is medicine. Medical schools from coast to coast have issued statements regarding this ruling, because of the important role that diversity plays in medicine. Measurable benefits have been observed when population demographics match medical care provider demographics, such as increased satisfaction and trust reported by patients. Due to this critical need for diversity within the medical field, many schools have stepped forward to discuss how this need will be met in the wake of the Supreme Court decision.
[Andrew] That’s right. While they cannot use race as a factor, socioeconomic status and parental levels of education are still acceptable criteria for consideration, and students may continue to write about life experiences in admissions essays. As well, some schools have implemented financial support or guarantees for high-achieving students. Despite this ruling, institutions are committed to ensuring diversity and inclusion across campuses, and the importance of representation among healthcare workers is not forgotten. Next, let’s take a closer look at artificial sweeteners.
In early 2023, reports of an artificial sweetener, erythritol, were linked to potential increases in heart disease outcomes. Now, concerns have been raised regarding aspartame, another artificial sweetener. Aspartame, commonly found in chewing gums and diet drinks, is set to be classified as a potential carcinogen by the World Health Organization (WHO).
There is a mixed body of evidence regarding aspartame’s carcinogenicity, where some studies find no link between aspartame and cancer, while others do. The WHO has 4 groups of carcinogenicity, ranging from carcinogenic to not classifiable as carcinogenic, and aspartame is set to join group 2b, as possibly carcinogenic. Other compounds in group 2binclude aloe vera and occupational hazards such as gasoline. One potential oversight is that these classifications do not consider the amount consumed, meaning that despite this classification, aspartame may be safe when consumed in up to 40 mg/kg of body weight. For reference, about 190 mg of aspartame is found in a can of Diet Coke.
So, if aspartame is possibly carcinogenic, why use it at all?
[Deepti] Since aspartame is an artificial sweetener, it reduces the amount of sugar needed to sweeten beverages and foods. This results in health benefits such as short-term weight management, which can be beneficial for obesity. As well, aspartame and other artificial sweeteners can be beneficial for those who monitor their blood sugar, such as individuals with diabetes. Artificially sweetened foods can be a way for individuals to enjoy sweet treats without significantly impacting blood sugar or excess calorie consumption. Ultimately, despite this latest classification by the WHO, more evidence is needed to truly assess whether aspartame is dangerous. For now, it represents a useful ingredient for those with obesity or diabetes but must be consumed in moderation. Now, we’ll discusss how Tyler Labine, star of “New Amsterdam”, had a raging stomach ache that was later found to be a dangerous blood clot. Thankfully Labine was treated in the emergency room and is currently recovering.
Blood clots are normal when we bleed, for it is the clotting of blood that prevents further bleeding and is part of the recovery process. They become very dangerous when they occur in the blood and do not naturally dissolve. They can impair blood flow to areas of the body blocked by the clot, and result in loss of oxygen and nutrients to that area, with eventual death of cells in that area. Heart attacks, strokes, and pulmonary embolisms are fatal events that are all caused by blood clots, resulting in a lack of oxygen and nutrients to cells of the heart, brain, or lungs.
Due to the complications of blood clots, minimizing one’s risk is very important. Periods of immobility, surgery, pregnancy, and genetic factors can increase the risk of developing blood clots. To lower the risk of blood clots, reducing the time spent immobile, and avoiding a sedentary lifestyle can help. As well, using compression stockings and medication as advised by a doctor, can help to lower risk.
[Andrew] And its not just Tyler Labine. Despite leading healthy lifestyles, athletes Chris Bosh and Serena Williams are celebrities who have battled blood clots. Bosh, a former Miami Heat star, battled blood clots in his lungs and his calf, which ultimately ended his career due to safety issues. Serena Williams endured a harrowing experience when giving birth, as shortly after her C-section, she developed a blood clot in her lung. Fortunately, both of these athletes were able to recognize the signs of blood clots, including shortness of breath, coughing, pain, redness, and swelling in a limb. Recognizing these signs and symptoms can be life-saving since time is very important when treating blood clots. Last but not least, let’s talk about how Australia is preparing for the inception of a new paradigm in mental health treatment.
[Deepti] Absolutely. Australia will now be the first country in the world to legalize the clinical prescription of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA )and psilocybin for mental health disorders. MDMA and psilocybin are commonly used illicitly, as ecstasy, and magic mushrooms. This has not deterred Australian regulatory boards, who are putting faith in clinical trial data showing that psilocybin is effective in combatting treatment-resistant depression, though significant side effects were noted. MDMA was shown to be effective in treating post-traumatic stress disorder alongside therapy.
Despite some evidence, the legalization of these medications has drawn some criticism. Critics suggest that more information is needed to determine which individuals may benefit from treatment, as well as how to mitigate side effects and negative experiences with the drugs. Treatment will also require the presence of a therapist and may cost around USD 660 per session.
In the USA, psychedelics are not approved for treatment, however, clinical trials have been conducted to determine whether they are an effective treatment. Oregon and Colorado have legalized magic mushroom use, despite the lack of FDA approval. The FDA has expressed some acceptance of the idea to explore psychedelic use, having published a guideline for clinical investigations with psychedelic drugs. One concern that critics have with the evaluation of psychedelics for psychiatric treatment, is that treatments are difficult to placebo control.
[Andrew] In a nutshell, for the approval of drugs, the FDA typically requires two groups that are identical, except one group receives the drug and the other receives a placebo, to prevent bias. In this case, because of the psychoactive effects of these drugs, both the patients and the psychiatrists know who is receiving the drugs and so bias seems impossible to avoid. With guidance from the FDA, some clinical trials have developed alternative methods to assess the efficacy of these treatments. Now that Australia has taken this first step, the rest of the world’s drug regulatory agencies will watch closely and continue the journey toward potentially legalizing psychedelics for medical purposes.
We’d like to acknowledge the following members of our team for their contributions to this week’s episode
- Neerav Mullur
- Benjamin Lam
- Kiera Liblik
Thank you for joining us today for this episode of the 2 Minute Medicine Podcast. New episodes come out every other week and all of our content has been curated and written by practicing physicians.
Please head to our website at 2minutemedicine.com to learn more and to access all of our content including medical study summaries, visual abstracts, excerpts from our Classics book series which is available on Amazon, and The Scan, which is our medical newsletter.
Thank you so much once again. To make sure that you don’t miss any of our content please subscribe and follow us on Twitter or Instagram @2MinMed
©2023 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.



![2MM: AI Roundup- AI Cancer Test, Smarter Hospitals, Faster Drug Discovery, and Mental Health Tech [May 2nd, 2025]](https://www.2minutemedicine.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/Untitled-design-350x250.png)




