#VisualAbstract: Immune dysfunction is associated with a higher risk of breakthrough COVID-19 infection
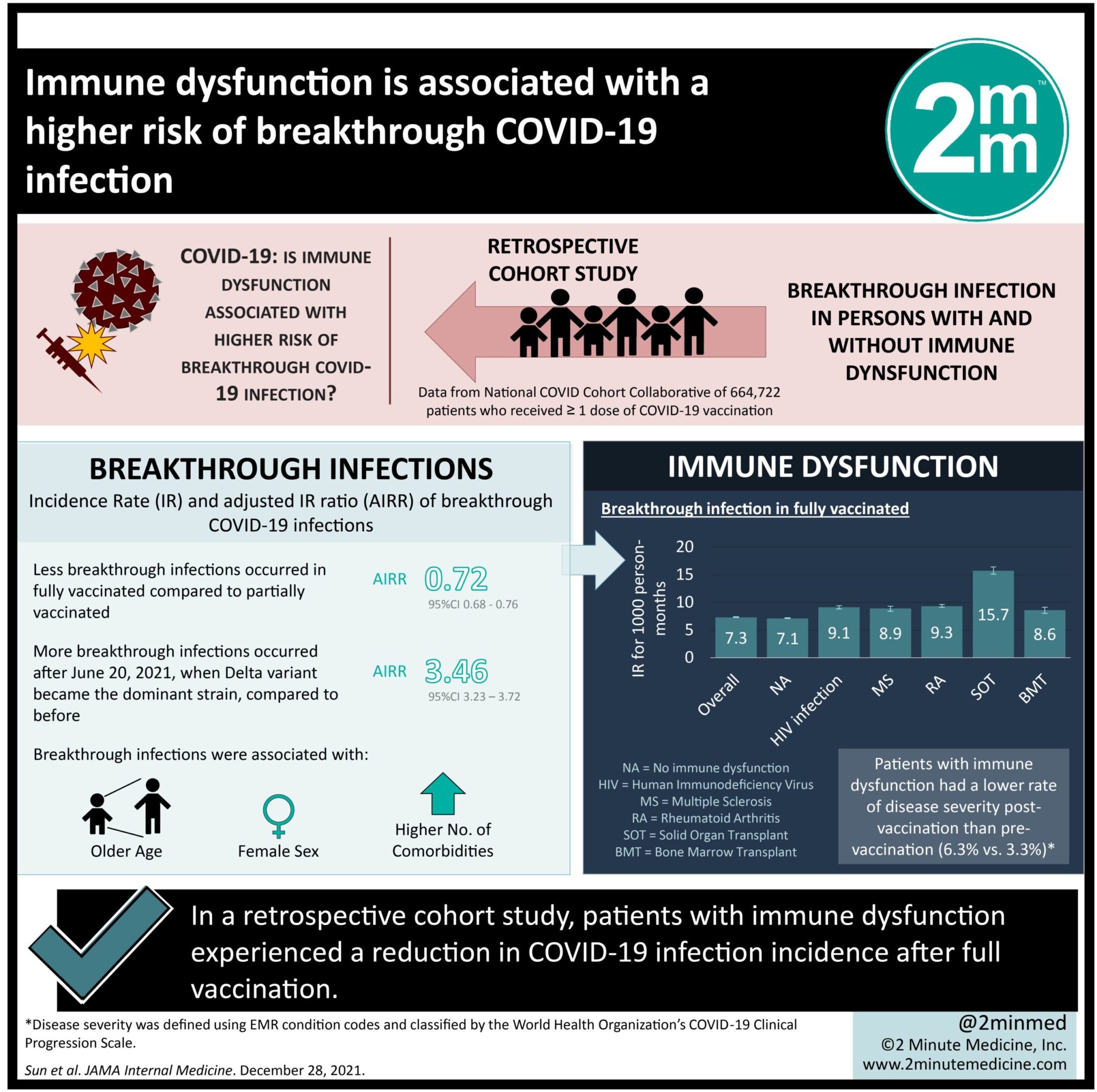
1. This retrospective cohort study found that patients with immune dysfunction experienced a reduction in COVID-19 infection incidence after full vaccination.
2. The incidence rate of infection after full vaccination in individuals with immune dysfunction was substantially higher compared to that in individuals without immune dysfunction.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Study Rundown: Breakthrough infection is defined as an infection that occurs after vaccination against a certain pathogen. It has been theorized that immune dysfunction may increase the risk of developing severe outcomes after COVID-19 infection, however conclusions cannot be drawn because these patients have largely been excluded from vaccination trials. One proposed mechanism for this is that individuals with immune deficiency mount a suboptimal immune response to the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, thus making them more susceptible to the virus. This study investigates the incidence rate (IR) and adjusted IR ratio (AIRR) of breakthrough COVID-19 infection in persons with, compared to without, immune dysfunction. COVID IR and severity, measured by proxy as hospitalization, was taken from the National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C) Data Enclave up to September 16, 2021 for those with and without immune dysfunction. Patients with immune dysfunction included human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) patients, those receiving solid organ transplant (SOT), patients with autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis (MS) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and cancer patients receiving bone marrow transplantation (BMT). Of the 664,722 individuals in the database, 5.3% had immune dysfunction. 90% of the sample received a full set of doses of mRNA vaccines. The sample represented 4,436,139 person-months where 5.0 breakthrough infections occurred per 1000 person-months and the average breakthrough occurred 138 days after full vaccination. There was a greater IR of breakthrough infections in those with, compared to without, immune dysfunction that was independently associated with HIV, RA, and SOT. HIV, SOT, and BMT patients experienced breakthrough infections earlier than non-immune dysfunctional patients. Vaccination reduced COVID hospitalizations in patients without immune dysfunction but increased them in patients with immune dysfunction. This study had several limitations. There was a potential for misclassification as the electronic medical record database may be inaccurate for vaccination at non-hospital sites that do not use the record like pharmacies. Additionally, this bias could be differential because immune-compromised patients may be more likely to go to hospitals for vaccination than non-immune dysfunctional patients. There is a significant confounding variable present in this retrospective cohort study as immunosuppressed patients likely have fewer contacts than those with functional immunity, thus conclusions can only be drawn about IR and not about likelihood of infection.
Click to read the study in JAMA Internal Medicine
Click to read an accompanying editorial in JAMA Internal Medicine
Relevant Reading: Managing Disease-Modifying Therapies and Breakthrough Activity in Multiple Sclerosis Patients During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Toward an Optimized Approach
In-Depth [retrospective cohort]: Self-reported demographic characteristics, pre-existing comorbidities, vaccination status, COVID diagnosis and hospitalization from at least single vaccinated individuals were collected from the N3C database. This study compared the rates of COVID infection and severity between pre- and post-vaccinated patients with and without immune dysfunction. 90% of the sample (N = 664,722 = 4,436,139 person-months) received a full set of doses of an mRNA vaccine. Those with SOT, BMT, or RA groups were older than those without immune dysfunction. Participants with HIV or SOT were more frequently non-Hispanic Black. Those with immune dysfunction had more comorbid health conditions. 5.0 breakthrough infections occurred per 1000 person-months. Fully vaccinated persons experienced a 28% lower risk of breakthrough infection compared to partially vaccinated individuals (AIRR = 0.72, 95% CI = 0.68-0.76). The rate of breakthrough infections was greater in the time after the Delta variant emerged as the dominant strain than the period before (before: IR = 2.2 vs after: IR = 7.3 per 1000 person-months; AIRR = 3.46; 95% CI = 3.23-3.72). Breakthrough infections were associated with older age, being female, and having a greater number of comorbidities. Individuals without immune dysfunction had a lower rate of breakthrough infections than those with immune dysfunction (IR = 7.1, 95% CI = 7.1-7.2 vs HIV: IR = 9.1, 95% CI = 8.8-9.4 per 1000 person-months, MS: IR = 8.9, 95% CI = 8.4-9.3, RA: IR = 9.3, 95% CI = 9.1-9., SOT: IR = 15.7, 95% CI = 15.1-16.4, BMT: IR = 8.6, 95% CI = 8.0-9.1 per 1000 person-months), especially of the Delta variant. Breakthrough infection was associated with each of HIV infection (AIRR = 1.33, 95% CI = 1.18-1.49), RA (AIRR = 1.20, 95% CI = 1.09-1.32), and SOT (AIRR = 2.16, 95% CI = 1.96-2.38). Infection with COVID-19 before vaccination reduced the risk of future infection after vaccination by 56% compared to no pre-vaccination infection (AIRR = 0.44, 95% CI = 0.40-0.48). In this sample, the average time to breakthrough infection was 138 days, with 2.8% of vaccinated patients contracting COVID within 6 months. Patients with immune dysfunction, particularly HIV, SOT, or BMT had a shorter time to breakthrough infection and a greater proportion of breakthrough infection than those without immune dysfunction; for example, 6% of vaccinated SOT patients contracting COVID within 6 months. There were fewer COVID hospitalizations after vaccination than before in patients without immune dysfunction (16.0% vs 24.4%), while there were more COVID hospitalizations after vaccination in those with immune dysfunction (6.3% vs 3.3%), but a decline in severity of those cases.
©2021 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.