#VisualAbstract: Trends in the prevalence of Hepatitis C infection during pregnancy and maternal-infant outcomes in the US, 1998 to 2018
 1. The prevalence of Hepatitis C infection during pregnancy increased between 1998 and 2018, coinciding with the opioid epidemic.
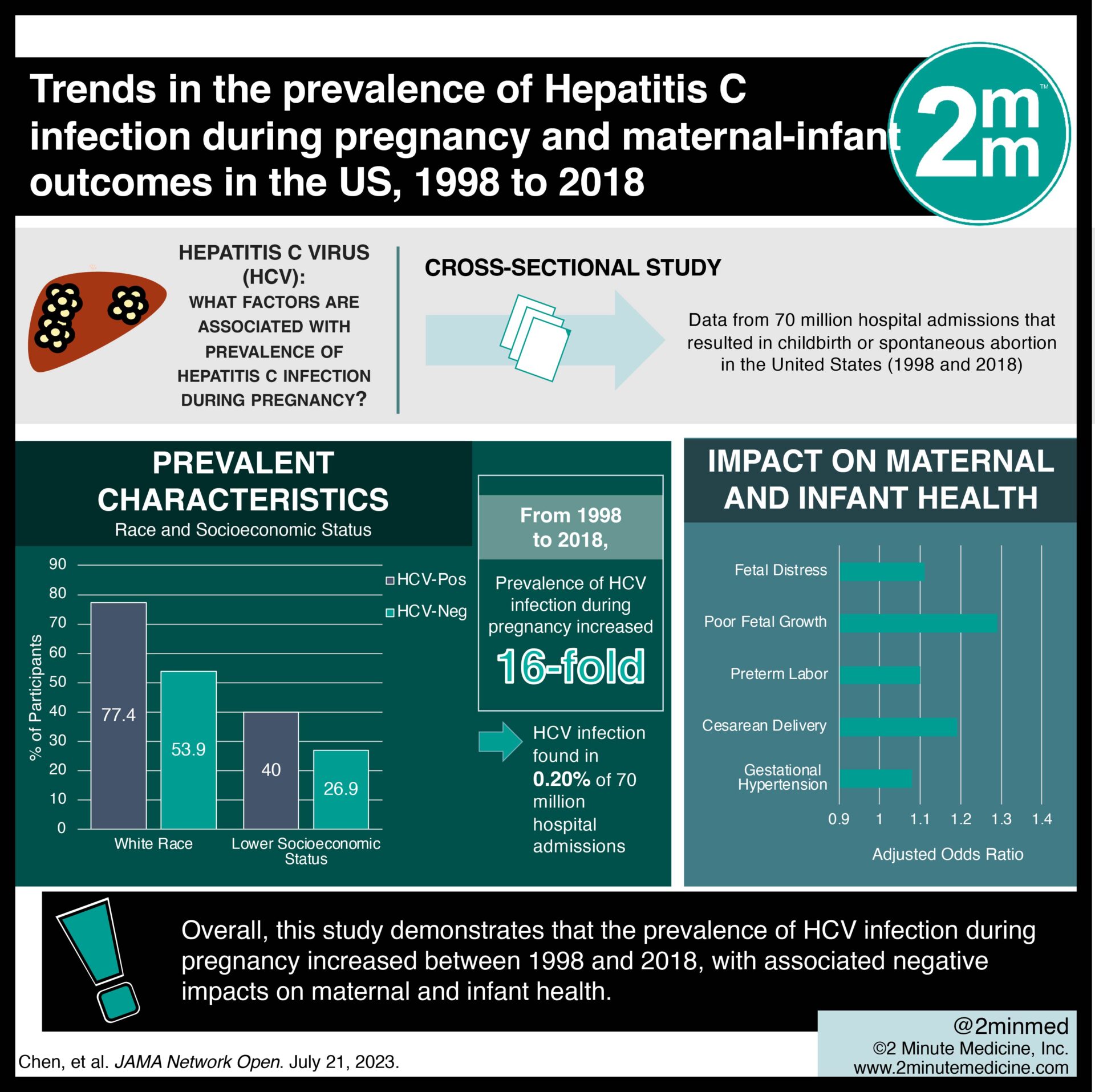
1. The prevalence of Hepatitis C infection during pregnancy increased between 1998 and 2018, coinciding with the opioid epidemic.
2. Individuals of White race, lower socioeconomic status, and a history of substance use were more likely to be infected with Hepatitis C during pregnancy.
3. Hepatitis C Infection was associated with a greater risk of gestational hypertension, cesarean delivery, preterm labour, poor fetal growth, and fetal distress.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Study Rundown: Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is the most prevalent chronic bloodborne infection in the United States. Injection drug use is the strongest risk factor for acquiring HCV. Antepartum opioid use has increased since the start of the opioid epidemic; however, data on the true prevalence of HCV infection during pregnancy and its impact on maternal and infant health is limited. Researchers aimed to trend the annual prevalence of HCV-positive pregnancies and identify HCV-associated maternal and infant outcomes. The prevalence of HCV infection during pregnancy increased 16-fold from 1998 to 2018. Risk factors associated with HCV-positive pregnancy included White race, lower income, and a history of substance use. HCV infection was associated with increased risks for both the mother and infant, including gestational hypertension, cesarean delivery, preterm labour, poor fetal growth, and fetal distress. Overall, this study demonstrates that the prevalence of HCV infection during pregnancy increased between 1998 and 2018, with associated negative impacts on maternal and infant health. One limitation of this study is that data were only collected from hospital admissions, excluding participants who give birth in other settings, such as home births. It is also important to recognize that HCV screening practices improved over time during the study period, which may have skewed the prevalence data. Future research may assess the efficacy of programs for HCV screening and care during pregnancy, particularly for those with substance-use disorders and lower socioeconomic status.
Click here to read the study in JAMA Network Open
In-Depth [cross-sectional study]: This cross-sectional study included data from 70 million hospital admissions that resulted in childbirth or spontaneous abortion in the United States between 1998 and 2018. Data were collected from the National Inpatient Sample of the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project. Over the course of the study period, the prevalence of HCV infection during pregnancy increased 16-fold. Overall, HCV infection was found in 0.20% of the 70 million hospital admissions (95% CI, 0.19%-0.21%). Specific characteristics were more prevalent among HCV-positive compared to HCV-negative participants, including White race (77.4%; 95% CI, 76.1%-78.6% vs 53.9%; 95% CI, 52.6%-55.1%), and lower socioeconomic status (40.0%; 95% CI, 38.6%-41.5% vs 26.9%; 95% CI, 25.8%-27.9%). Additionally, substance use was an important risk factor for HCV infection in pregnancy. HCV-positive participants were more likely to have a history of tobacco (41.7%; 95% CI, 40.6%-42.9% vs 4.0%; 95% CI, 3.8%-4.2%), alcohol (1.8%; 95% CI, 1.6%-2.0% vs 0.1%; 95% CI, 0.11%-0.12%), opioid (28.9%; 95% CI, 27.3%-30.6% vs 0.3%; 95% CI, 0.25%-0.29%), and cocaine (6.9%; 95% CI, 6.4%-7.4% vs 0.3%; 95% CI, 0.26%-0.30%) use. After adjusting for confounding variables including substance abuse, maternal HCV infection was associated with a greater risk of gestational hypertension (AOR 1.08; 95% CI, 1.03-1.14), cesarean delivery (AOR 1.19; 95% CI, 1.15-1.22), preterm labor (AOR 1.10; 95% CI, 1.05-1.14), poor fetal growth (AOR 1.29; 95% CI, 1.21-1.37), and fetal distress (AOR 1.11; 95% CI, 1.08-1.15).
©2023 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.







