#VisualAbstract: Upadacitinib plus topical corticosteroids is safe and effective for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis;
1. Upadacitinib combined with topical corticosteroids reduced Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) and Investigator’s Global Assessment for atopic dermatitis (vIGA-AD) scores significantly more than placebo with corticosteroids.
2. Efficacy of upadacitinib combination therapy was comparable to upadacitinib monotherapy, suggesting potential for steroid-sparing treatment of atopic dermatitis.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
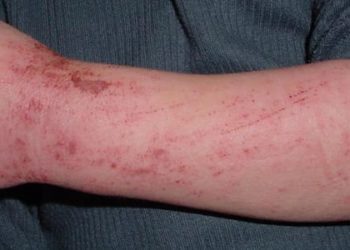
Study Rundown: For patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (eczema), topical corticosteroids combined with systemic therapy is typically the first line treatment regimen. Upadacitinib is an oral JAK inhibitor used to treat immune-mediated inflammatory conditions that is currently being investigated for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 clinical trial (AD Up) evaluated the safety and efficacy of Upadacitinib (15 mg or 30 mg) combined with topical corticosteroid therapy compared to placebo combination therapy for the treatment of atopic dermatitis for 16 weeks. Treatment response was measured using 75% reduction in EASI score from baseline (EASI-75) and vIGA-AD response scores of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) with at least two grades of improvement compared to baseline. Secondary endpoints included score changes assessed at various time points during the study. Treatment response to Upadacitinib 15 mg and 30 mg with topical corticosteroids were superior to placebo with topical corticosteroids at the end of 16 weeks, with over 65% of patients achieving an EASI-75 response and over 40% vIGA-AD response. Patients were also able to discontinue corticosteroid use over the course of the study. Both treatment regimens were well tolerated, with severe adverse events reported for <1% of the study population. Common adverse effects included acne, nasopharyngitis, and upper respiratory infection. The results of this trial demonstrate the efficacy and safety of two doses of Upadacitinib plus topical corticosteroids for the treatment of atopic dermatitis, encouraging future studies on Upadacitinib-based steroid-sparing treatment regiments.
Click to read the study in The Lancet
Relevant Reading: Upadacitinib in adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: 16-week results from a randomized, placebo-controlled trial
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: This clinical trial was conducted at 171 clinical centers across 22 countries. 901 patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, defined as ≥10% of body surface area, EASI score ≥16, and vIGA-AD score ≥3). Patients were randomly assigned 1:1:1 to two treatment groups (Upadacitinib 15 mg [n=300] or 30 mg [n=297] plus topical corticosteroids) or placebo group (placebo plus topical corticosteroids; n=304) for a 16-week treatment period. Treatment was given orally once daily, and patients were assessed for corticosteroid discontinuation as symptoms stabilized. At 16 weeks, a significantly greater proportion of patients in both upadacitinib groups achieved a EASI-75 and vIGA-AD response compared to placebo. The adjusted difference in EASI-75 response for the 15 mg treatment group was 38.1% (95% CI 30.8 – 45.4, p<0.0001) and 50.6% (43.8 – 57.4, p<0.0001) for the 30 mg group. The adjusted difference in vIGA-AD response for the 15 mg treatment group was 28.5% (22.1 – 34·9, p<0.0001) and 47.6% (41.1 – 54.0, p<0.0001) for the 30 mg treatment group. Additionally, the median time to first discontinuation of topical steroids was shorter in both treatment groups compared to placebo (15 mg median 88 days IQR [73–not estimable], 30 mg median 57 days [41–59], placebo median not estimable [120–not estimable], p <0.0001 for both treatment groups). No deaths were reported in either treatment group, with severe adverse reactions that resulted in treatment discontinuation occurring for only 1% of patients. The results of this trial are limited by the 16-week follow-up period, as atopic dermatitis requires long-term systemic management. However, this trial provides compelling evidence for the efficacy of Upadacitinib as a systemic therapy for the treatment atopic dermatitis, both in reducing disease burden and reducing the need for topical corticosteroids.