Voriconazole superior to amphotericin B for invasive aspergillosis [Classics Series]
1. In immunocompromised patients with invasive aspergillosis, treatment with voriconazole was found to be superior to amphotericin B in achieving successful outcomes.
2. The incidence of serious adverse events was significantly lower in patients in the voriconazole group, as compared with those in the amphotericin B group.
Original Date of Publication: August 2002
Study Rundown: In immunocompromised patients, like those with prolonged neutropenia and previous transplant recipients, invasive aspergillosis is a dangerous and not uncommon complication affecting between 5% to 20% of patients deemed high-risk. For many decades, the standard therapy for invasive aspergillosis infections has been amphotericin B, despite limited success with the treatment and significant risk of toxicity (e.g., fevers/chills, hypotension, kidney injury, hepatotoxicity, cardiac arrhythmias). Prior to this trial, voriconazole had been shown to be somewhat effective in treating invasive aspergillosis, though no randomized trials had been performed. The purpose of this randomized, controlled trial was to compare the effects and safety of voriconazole with amphotericin B in the primary treatment of immunocompromised patients presenting with acute invasive aspergillosis.
In summary, patients treated with voriconazole were significantly more likely than those on amphotericin B to experience a successful outcome. Moreover, while the trial primarily sought to demonstrate non-inferiority, it was able to demonstrate that voriconazole was superior to amphotericin B in the treatment of invasive aspergillosis. Patients in the voriconazole group also experienced significantly fewer adverse events as compared with those in the amphotericin B group. Based on the findings of this study, the Infectious Diseases Society of America currently recommends that voriconazole be the primary treatment of invasive aspergillosis in most patients.
Click to read the study in NEJM
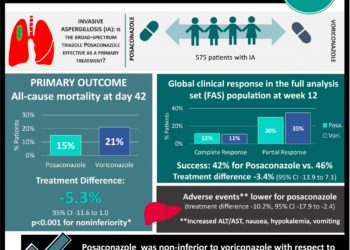
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: A total of 277 patients from 95 centers in 19 countries were included in the modified intention-to-treat population, with 144 in the voriconazole group and 133 in the amphotericin B group. Patients were eligible if they were ≥12 years of age, had definite or probable invasive aspergillosis, and were immunocompromised (e.g., allogeneic hematopoietic-cell transplantation, hematologic cancer, aplastic anemia, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome – AIDS, solid-organ transplantation). Exclusion criteria included chronic aspergillosis, aspergilloma, allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, previous systemic therapy with amphotericin B/itraconazole, treatment with interacting drugs (e.g., rifampin), hypersensitivity to azoles or amphotericin B, aminotransferase/bilirubin/alkaline phosphatase level >5 times the upper limit of normal, serum creatinine >221 μmol/L (2.5 mg/dL), and pregnancy. Patients in the voriconzole group received 6 mg/kg intravenously twice daily on day 1, followed by 4 mg/kg intravenously twice daily for at least 7 days, and 200 mg orally twice daily afterwards. Those in the amphotericin B group received 1.0-1.5 mg/kg intravenously daily. Planned duration of therapy was 12 weeks, and patients could have been treated with other antifungals should they experience toxicity from treatment or poor response to therapy. The primary aim of the study was to demonstrate non-inferiority of voriconazole as compared with amphotericin B, while the secondary aim was to demonstrate superiority of voriconazole.
At week 12, patients in the voriconazole group were significantly more likely to have a successful outcome than those on amphotericin B (52.8% vs. 31.6%, absolute difference 21.2%, 95%CI 10.4 to 32.9%). Given these findings, voriconazole was found to be superior to amphotericin B for invasive aspergillosis. The survival rate at week 12 was also significantly higher in the voriconazole group (70.8% vs. 57.9%; HR 0.59, 95%CI 0.40-0.88). There were significantly fewer adverse events in patients taking voriconazole as compared with those taking amphotericin B (p = 0.02). Although those on voriconazole experienced significantly higher instances of visual disturbances (44.8% vs. 4.3%, p < 0.001), all these events resolved without intervention.
Image: PD
©2015 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.