Tirzepatide reduces body weight and improves cardiometabolic function in patients with obesity
1. Tirzepatide treatment significantly reduced body weight and fat composition in obese patients while improving cardiometabolic risk factors and physical function.
2. The frequency of serious adverse events was not significantly different between the tirzepatide and placebo groups.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: The global prevalence of obesity is increasing substantially. This is detrimental to global health as obesity is associated with several chronic conditions such as cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists, which target food-stimulated hormonal pathways, are an emerging drug class for treating obesity and diabetes. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptor agonists also regulate energy balance via similar mechanisms. A combination of these two drug classes is hypothesized to produce synergistic effects on weight loss. The present phase three randomized control trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of various doses of tirzepatide, a dual GLP-1 and GIP receptor agonist, as compared to placebo control. In addition to standard lifestyle intervention, participants received once weekly subcutaneous doses of tirzepatide (5mg, 10mg, and 15mg) or a placebo for 72 weeks. Participants were followed for four weeks after the regimen. Tirzepatide significantly reduced body weight and fat composition compared to placebo. Tirzepatide treatment was also associated with improvements in cardiometabolic risk factors and physical function. A higher proportion of participants in the treatment group experienced adverse events, of which the most common were gastrointestinal-related symptoms. However, the prevalence of serious adverse events was statistically similar between groups. As a limitation, the effect of tirzepatide on overweight (body-mass index (BMI) of 27 to 30) patients is not well supported as overweight participants only made up 5.5% of the study. Efficacy and safety data may also have limited generalizability to older patients due to the high proportion of young participants in the study cohort.
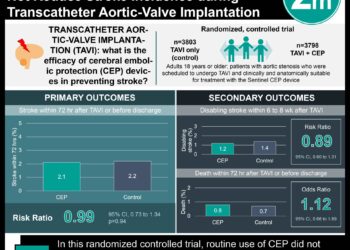
Click to read the study in NEJM
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: In the present study, adult patients with obesity (n=2,539) were randomly assigned in a 1:1:1:1 ratio into tirzepatide (5mg, 10mg, or 15mg) or placebo groups. Participants were administered tirzepatide or placebo subcutaneously once weekly concurrently with a standard lifestyle intervention for 72 weeks. Safety data were collected during a four-week follow-up period for participants without prediabetes. In total, 86% of participants completed the trial treatment. At baseline, the majority of participants had a BMI of over 30 (94.5%) and did not have prediabetes (59.4%). At week 72, weekly 5mg, 10mg, and 15mg dose of tirzepatide resulted in a -15% (95% Confidence Interval [CI], -15.9 to -14.2), -19.5% (95% CI, -20.4 to -18.5), and -20.9% (95% CI, -21.8 to -19.9) weight reduction, respectively. Placebo resulted in a -3.1% (95% CI, -4.3 to -1.9) weight reduction. All three doses of tirzepatide resulted in a significant weight reduction compared to the placebo (p<0.001 for all comparisons to placebo). Body fat composition was also reduced by 33.9% in the tirzepatide group compared to 8.2% in the placebo group. Tirzepatide treatment was associated with improvements in cardiometabolic risk factors, including waist circumference, blood pressure, fasting insulin level, and lipid levels. Participants in the tirzepatide group also had improved perception of their physical function as assessed by the 36-Item Short Form Health Survey. Finally, adverse events were reported in 78.9% to 81.8% of participants in the tirzepatide group compared to 72.0% of participants in the placebo group. The most common adverse events were gastrointestinal. However, the prevalence of serious adverse events was similar between groups. This clinical trial supports the efficacy and safety of tirzepatide, a dual GLP-1 and GIP agonist, as a treatment for obesity in younger patients.
Image: PD
©2022 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.