Vitamin D effective in preventing the progression of pre-diabetes to diabetes
1. The current systematic review and meta-analysis found that vitamin D supplementation for pre-diabetic patients is associated with a reduced risk of progression to diabetes.
2. Vitamin D supplementation was also associated with improved glucose regulation in this population.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Type 2 diabetes mellitus is becoming increasingly prevalent on a global scale. Notably, type 2 diabetes is associated with an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease, multi-organ dysfunction, and adverse cardiovascular events. Although effective treatments exist, efforts have been in place to reduce the incidence of diabetes as a primary prevention strategy. Individuals with borderline elevated blood glucose, known as pre-diabetics, are at a particularly high risk of developing diabetes if preventative measures are not implemented. Aside from lifestyle modifications, higher vitamin D levels have been observed to be associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes. The current study was a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, based on the individual participant data (IPD) approach, to assess whether vitamin D could decrease the risk of developing diabetes among adults with prediabetes. Accordingly, three trials were included and their data were extracted and analyzed. The main findings were that participants receiving vitamin D supplementation were less likely to develop diabetes and more likely to regain normal glucose regulation. Vitamin D was not associated with an increased risk of adverse events. Overall, this systematic review and meta-analysis found that vitamin D supplementation may be beneficial among pre-diabetic patients in preventing the progression to diabetes and improving glucose regulation.
Click here to read the study in AIM
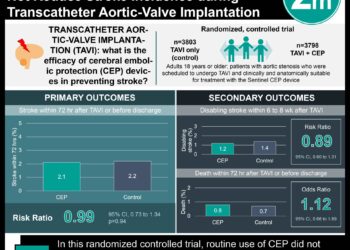
In-Depth [systematic review and meta-analysis]: The current study was a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials that investigated the effect of oral vitamin D supplementation in adults with pre-diabetes on the development of diabetes. The primary outcome to be extracted from these trials was the time to event for new-onset diabetes. In total, three randomized trials were identified and included for data synthesis, encompassing 4,190 participants with approximately 1:1 ratio between the vitamin D and placebo groups. Vitamin D supplementation was provided in the form of cholecalciferol 20,000 IU weekly, cholecalciferol 4,000 IU daily, or eldecalcitol 0.75 mcg daily. All three trials were assessed to have a low risk of bias. The median follow-up period was 3 years. It was found that vitamin D resulted in a 15% reduction in the risk of new-onset diabetes (Hazard Ratio [HR], 0.85; 95% Confidence Interval, [CI] 0.75 to 0.96) and a three-year absolute risk reduction of 3.3 percentage points (95% CI, 0.6 to 6 percentage points). Two trials utilized cholecalciferol as supplemental vitamin D, which requires conversion to 25-hydroxyvitamin D in the body for bioactivity. Among their participants receiving supplemental vitamin D, those who maintained the mean serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level of 125 nmol/L or higher had their risk development diabetes reduced by 76% (HR, 0.24; 95% CI, 0.16 to 0.36), compared to those whose serum levels were between 50 to 74 nmol/L. The three-year absolute risk reduction was 18.1 percentage points (95% CI, 11.7 to 24.6; percentage points). Vitamin D also increased the likelihood of regaining normal glucose regulation by 30% (rate ratio, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.16 to 1.46). Lastly, vitamin D supplementation was not associated with an increased risk of adverse events. In summary, this systematic review synthesized evidence supporting the use of vitamin D supplementation to reduce the risk of diabetes among individuals with pre-diabetes.
Image: PD
©2023 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.